In-Depth Look at Triceratops: Characteristics and Impact
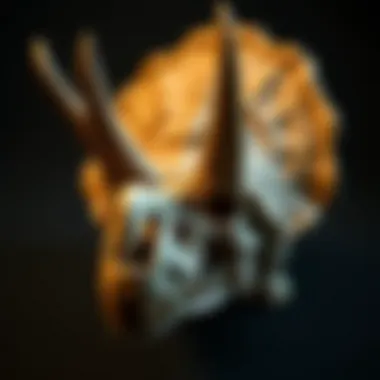

Intro
The Triceratops stands out in the vast pantheon of dinosaurs, capturing the imagination of both scientists and the general public alike. Known for its impressive three-horned visage and a characteristic frill, this dinosaur roamed the earth during the late Cretaceous period. As we dig into its intricacies, we unearth not just the story of a distinct species but also a window into the ecological and evolutionary dynamics of its time.
To begin with, understanding the Triceratops means delving into its physical characteristics— the very traits that distinguish it from both contemporaneous species and modern fauna. This provides an insight into its lifestyle, its complaints with predators, and its role within its habitat. The connection to habitat becomes evident once we grasp its dietary choices–a creature mainly herbivorous, it thrived in lush landscapes that supported ample flora, showcasing evidence that the environment heavily shaped its adaptations.
Beyond the biological aspects, the behavior of Triceratops offers another layer of intrigue. Did it roam in herds or prefer solitude? Understanding interactions among individuals could illuminate its social structures and survival strategies. Moreover, its significance in paleontology is immense, paving the way for notable discussions about evolutionary relationships with other ceratopsids and the various discoveries that continue to challenge established narratives.
Finally, this exploration can't omit the cultural impact Triceratops has left behind. From jurassic comics to blockbuster films, its image has permeated popular culture in a way few other dinosaurs have managed. This fusion of science with societal representation renders the Triceratops not simply an object of study, but a vibrant symbol of the ancient past.
Prepare to delve deeper into the complexities of the Triceratops as we begin to unpack each aspect further, revealing layers of insight that go far beyond the basic credentials of this recognizable dinosaur.
Foreword to Triceratops
The Triceratops has captured the imaginations of both young and old, often being a staple character in books and films about prehistoric life. Beyond its captivating aesthetic, this dinosaur stands as a symbol of the incredible diversity that existed during the Cretaceous period. Its three distinctive facial horns and large frill are not just for show; they served critical purposes in its daily life, from defense against predators to possibly playing a role in social interactions among herd members.
Understanding the Triceratops also deepens our appreciation of the complex ecosystems that thrived millions of years ago. The study of this dinosaur opens the door to discussions about evolutionary biology and the intricate relationships that numerous species maintained within their environments. As we delve into its historical context and discovery timeline, it becomes evident that Triceratops was more than just a large herbivore; it was a pivotal player in its ecosystem, shaping both its surroundings and the evolutionary trajectories of other species.
Historical Context
When we talk about Triceratops, we are addressing a notable chapter in the story of dinosaurs. This beast roamed the North American landscape roughly 68 to 66 million years ago, during the late Cretaceous. At this time, the world was undergoing significant climatic changes, characterized by fluctuating sea levels and distinct habitats that fostered a rich array of flora and fauna. The emergence and eventual dominance of dinosaurs were influenced heavily by these changes. As Triceratops flourished in a warm, lush environment, it thrived among other dinosaurs, such as Tyrannosaurus rex and various species of hadrosaurs and theropods.
This historical backdrop enriches our understanding of why the Triceratops developed its unique features. The horns and frill, admired so often, were likely adaptations developed over generations as a response to environmental pressures, including predation and competition for food. By analyzing this dinosaur’s specific niche within its ecosystem, researchers can unearth valuable insights into the delicate balance of life that existed at that time.
Discovery Timeline
The journey to recognize Triceratops as one of the most illustrious dinosaurs began in the late 19th century. The first fossils were unearthed in 1887 in Colorado, marking a significant beginning for paleontology. The initial discovery piqued interest, though it wasn’t until researchers, like Othniel Charles Marsh, began formally documenting these finds that the importance of Triceratops was fully appreciated.
Over the course of several decades, additional fossils were discovered across various locations such as Montana and Wyoming. Each new find extended the understanding of its anatomical variations and offered clues to its biology and lifestyle. The 1890s alone saw the unveiling of several complete skeletons, and by the turn of the 20th century, Triceratops was firmly positioned in the public and scientific consciousness.
In recent years, modern technology like CT scans and 3D modeling has revolutionized how scientists examine Triceratops fossils. These advancements have let us glean even more information about its growth patterns, diet, and the way it might have interacted within its habitat. The story of its discovery is a dynamic narrative of science's evolving nature, illustrating how knowledge builds on itself through time.
Physical Characteristics
Understanding the physical characteristics of the Triceratops is essential for appreciating its evolutionary adaptations and its role in the Cretaceous ecosystem. These traits not only highlight the dinosaur's unique identity but also reflect the environmental conditions and challenges it faced during its time on Earth. Exploring these aspects can provide valuable insights into the biology of this species and how it maneuvered within its habitat. The discussion of Triceratops's physical features, particularly its distinctive frill and horns, body structure, and coloration theories, paints a vivid picture of this extraordinary creature.
Distinctive Features
Frill and Horns
The frill and horns of the Triceratops are perhaps its most defining attributes, setting it apart from many other dinosaurs. The large bony frill at the back of its head and the prominent horns above its eyes serve both protective and social functions. These features likely played a significant role in defense against predators, while also serving as visual indicators during social interactions with other Triceratops. What stands out about the horn arrangement is their variability; different specimens show differing horn shapes and sizes, suggesting a level of sexual dimorphism or individual variation. Including this analysis contributes depth to the understanding of Triceratops's evolutionary strategies in a competitive world.
"The frill and horns of Triceratops are not just for show—they are a testament to the ecological niches this magnificent creature occupied."
However, while these features may have been beneficial, they also brought challenges. The weight of the horns and frills could impact the animal's mobility, making it less agile in fleeing predators.
Body Structure
When discussing the body structure of Triceratops, one can't overlook its robust build. This dinosaur possessed a stout body with a broad torso, lending itself to significant muscle mass, which helped it support its heavy skull. Its four sturdy legs placed it in a prime position to sustain its weight and navigate varied terrains. An important facet of its body structure is its well-adapted digestive system, specifically suited for processing tough plant material, confirming its herbivorous lifestyle.
The overall structure of Triceratops reveals critical adaptations, allowing it to thrive in the lush habitats of its time. A broader body structure not only suggests strength but also indicates its ability to consume larger amounts of vegetation to sustain its energy needs.However, this same strong build could limit speed, particularly in escape situations.
Coloration Theories
Coloration theories surrounding the Triceratops are fascinating, offering clues about its behavior and habitat interactions. While direct evidence of skin color is absent, scientists speculate based on closely related species and fossilized impressions. Some theories suggest that Triceratops could have had a variety of colors ranging from earthy browns to more vivid patterns, depending on its environment and social needs.
This aspect is significant when considering camouflage. A more vibrant coloration could serve as a display mechanism, attracting mates or deterring rivals. Highlights of skin pigmentation can also hint at thermoregulation strategies; lighter shades might assist in reflecting sunlight, while darker hues could help absorb warmth.
Nevertheless, while these theories enrich our understanding, they remain speculative. Generating direct evidence through fossils or advanced imaging techniques might provide a clearer picture, warranting ongoing research in the field.
Size and Weight
The dimensions of Triceratops, specifically its size and weight, contribute to its ecological significance. Understanding how Triceratops compares to other dinosaurs can highlight its role within the food web and its adaptations for survival.
Comparison with Other Dinosaurs
Triceratops was a significant figure among the ceratopsid family, with adults typically weighing between 6 to 12 tons. When compared to other dinosaurs, such as the smaller herbivores or the towering theropods, it emerges as a remarkable example of size adaptation. Larger size often correlates with fewer natural predators, thus allowing Triceratops to thrive in a competitive ecosystem.
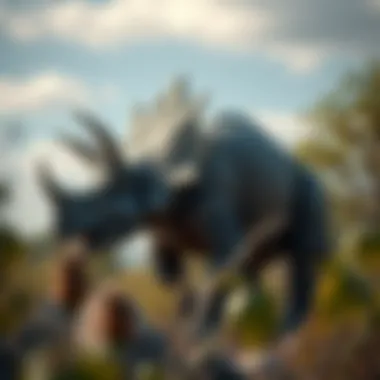

In the grand scheme, these comparisons are not just numbers on a scale; they narrate the evolutionary paths taken by different species within the Cretaceous period. Discussing size differences showcases specialization within the herbivore category, providing insights into dietary preferences and environmental adaptations, making it a useful aspect of this article.
Implications for Behavior
Size and weight have direct implications on the Triceratops's behavior and interaction with its environment. A larger body grants power but may compromise speed and agility, influencing feeding habits and social structures. The increased weight necessitates a high-calorie diet, leading to its herbivorous nature.
This weight also hints at its social behavior. Heavier specimens likely formed their own dynamics, possibly indicating that large males engaged in combat for dominance or mating rights. The very nature of these implications enriches our understanding of herbivorous dinosaurs, notably their survival strategies amidst predators and climatic changes.
Ultimately, the exploration of physical characteristics provides not just a glimpse into the life of Triceratops but also into the larger narrative of Cretaceous ecology, making it a fascinating area of study.
Habitat and Distribution
Understanding the habitat and distribution of Triceratops provides a window into the life of this remarkable dinosaur. The environments in which it lived not only shaped its physical adaptations but also influenced its interactions with other species. Knowledge of these aspects is crucial for anyone keen on paleontology, and it adds depth to our appreciation of the Cretaceous landscape.
Geographical Range
North America
North America was the primary geographical arena for Triceratops, particularly during the late Cretaceous period. This region, characterized by its vast plains and lush vegetation, offered Triceratops a promising habitat full of diverse foraging opportunities. The sheer variety of flora in North America, from cycads to flowering plants, contributed to the dinosaur’s herbivorous diet.
One of the key characteristics of this area is the Torrential Climate—an important factor that played a role in shaping the landscapes. The abundance of resources made North America an ideal home for not just Triceratops but many other dinosaur species too. However, the terrain varied, with some areas being prone to floods while others were bathed in arid conditions, showcasing how the landscape continuously transformed over time.
- Advantages: Rich biodiversity enhances understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
- Disadvantages: The environment's variability poses challenges in consistently tracing its evolution.
Climate During the Cretaceous
The climate during the Cretaceous period was predominantly warm, characterized by high sea levels and a greenhouse effect that led to lush ecosystems. This climatic condition is crucial for comprehending why Triceratops thrived in North America. The warmth allowed for widespread vegetation, which served as food for the herbivorous Triceratops.
A unique feature of this climate was the seasonal weather patterns. For instance, regions could experience dry spells followed by intense rain, which could rejuvenate the flora quickly. This phenomenon might have led to cyclical migrations for food and water resources, an aspect that influenced the social structure of Triceratops herds.
- Advantages: A warm climate fosters an environment where plant life can flourish.
- Disadvantages: Changes in climate can lead to extinction events, creating a volatile backdrop for survival.
Ecosystem Interactions
Flora of the Period
The flora during Triceratops’s time was vibrant and diverse. Plants such as ferns, cycads, and gnarled conifers made up a good part of the landscape, shaping the feeding habits of herbivorous dinosaurs. Understanding the plant life is as crucial as studying the dinosaurs themselves, as it lays the groundwork for grasping the entire ecosystem in which Triceratops lived.
The unique mix of these plants provided Triceratops with a myriad of feeding strategies, allowing it to adapt and thrive in competitive scenarios. Furthermore, the plant life itself adapted over time, reflecting the evolutionary pressures of the changing climate and the presence of herbivores like Triceratops.
- Advantages: Diverse plant life enhances the understanding of co-evolution.
- Disadvantages: Limited fossil records can complicate our understanding of plant-dinosaur interactions.
Predator-Prey Dynamics
The predator-prey dynamics during the Cretaceous period paint an intriguing picture of survival strategies. The presence of numerous predators, including Tyrannosaurus rex, meant that Triceratops had to develop defenses. The heavy frill and prominent horns offered some protection against these apex predators, suggesting that natural selection played a significant role in the evolution of its features.
This unique characteristic of having to constantly negotiate a dangerous ecosystem influenced not only its behavior but also its social interactions. For instance, whether in groups or solitary, its actions were likely shaped by the need to stay vigilant against threats. Understanding these dynamics offers valuable insights into its daily life and survival strategies.
- Advantages: Examining these relationships provides crucial insights into evolutionary pressures.
- Disadvantages: The fossil record is often incomplete, making conclusive statements difficult.
In studying the habitat and distribution of Triceratops, we gain a comprehensive understanding of how this dinosaur thrived within its unique environment and interacted with its surrounding flora and fauna.
Behavioral Patterns
Understanding the behavioral patterns of Triceratops provides a window into the life and ecology of this fascinating dinosaur. The behaviors exhibited by Triceratops, such as social structures and feeding habits, give paleontologists insights into how these creatures interacted with their environment and each other. Notably, analyzing these patterns aids in piecing together the larger picture of Cretaceous ecosystems, including the relationships between herbivores and their surroundings. This exploration enhances our grasp of the motives driving their existence, allowing for a deeper appreciation of their adaptability and resourcefulness.
Social Structure
Herds and Migration
The social dynamics of Triceratops likely revolved around their grouping in herds, which hold several significances. Herds could provide critical advantages for protection against predators. Imagine a tight-knit group moving together, offering safety in numbers. While there is still debate on the necessity of migration for Triceratops, those herding behaviors might hint at migratory patterns in search of food or water during dryer spells. Their strong social ties, possibly formed from familial bonds, could strengthen their survival.
The key characteristic of herds is the collective movement. It showcases how these dinosaurs might have shared resources effectively. Furthermore, the potential for migration could suggest a level of intelligence in locating seasonal feeding grounds. This aspect is beneficial for appreciating how Triceratops adapted to their environment.
One unique feature of herds is the social bonds within them. These relationships may also lead to cooperative care of the young, enhancing the group's overall success in raising offspring. The downside, however, could have been their increased visibility to predators, as larger groups may attract unwelcome attention. Overall, understanding herd dynamics may point to a richer social life than previously believed.
Territorial Behavior
Territorial behavior in Triceratops likely played a role in their ecological interactions. Unlike some dinosaurs that may have been highly nomadic, certain species of Triceratops could exhibit territorial instincts, defending specific areas for feeding and breeding. This characteristic allows us to consider how Triceratops managed their habitat and resources.
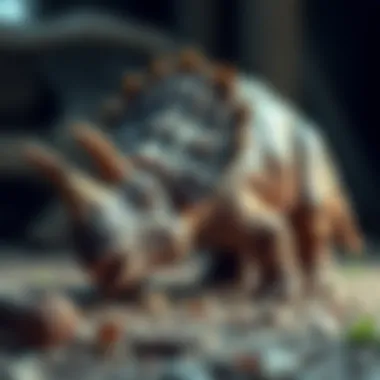

The act of defending territory suggests a strong instinct for survival and mating success. Territories could provide optimal feeding conditions, ensuring that a certain group has uninterrupted access to vital resources. This behavior is a beneficial addition to our understanding of their ecological niche. However, enforcing territory would necessitate energy exertion that could be better utilized for foraging or other necessary actions.
A unique aspect of territorial behavior is that it likely varies between whether they were solitary or social creatures, influencing how they established and maintained their areas. While territorial disputes could offer good competition among males for mating rights, they could lead to increased injuries, hence a balancing act in the struggle for dominance.
Feeding Habits
Herbivorous Diet
The herbivorous diet of Triceratops defines not only what they ate but also how they interacted with their surroundings. Being predominantly herbivores, they played a crucial role in shaping their ecosystem. By browsing on a variety of plants, Triceratops likely influenced vegetation patterns and distribution.
A highlight of their feeding habits is the ability to consume tough, fibrous plants, which would have included ferns and cycads. This dietary choice showcases their adaptability in the face of availability and competition. An herbivorous diet is integral to this article as it underscores their role in the food chain and ecosystem. Moreover, their specialized dentition and skull structure show how nicely evolved they were for their specific diet.
One unique feature of their diet is the potential for seasonal changes in feeding habits, which might indicate opportunistic behaviors. This could mean that during lean periods, Triceratops adapted by including a broader range of plant materials. However, relying heavily on dense foliage comes with disadvantages—such as potential resource depletion during periods of drought or environmental change.
Feeding Strategies
The feeding strategies employed by Triceratops reveal much about their adaptation to the Cretaceous environment. By utilizing specialized strategies that encompassed foraging and group feeding, they could maximize their energy intake effectively.
A critical aspect of these strategies is their capability to select specific plant materials based on availability. This flexibility is a valuable trait for survival, especially during climate fluctuations. Such adaptive feeding methodologies ensure they access adequate nutrients throughout different environmental conditions, which is crucial for their growth and development.
One unique behavior might include exploiting diverse food sources, possibly even scavenging on fallen fruits or vegetation. This versatility provides advantages during scarce periods. However, continuously changing feeding strategies might communicate vulnerability to environmental shifts, displaying how crucial it was for Triceratops to respond promptly to changes in their habitat.
In summary, the behavioral patterns of Triceratops—ranging from social structures to feeding habits—are multidimensional. These patterns enrich the narrative around their existence, nurturing a deeper understanding of the dynamics at play during the Cretaceous period.
Fossil Record and Significance
The fossil record of the Triceratops holds immense importance in piecing together the evolutionary puzzle of dinosaurs. It offers a tangible glimpse into the past, revealing how these magnificent creatures adapted, thrived, and faced extinction. Understanding the significance of fossils helps enthusiasts and collectors appreciate the dynamic history of life on Earth, as well as the ways in which these remnants inform current research in paleontology.
Notable Finds
Iconic Discoveries
One of the most significant aspects of Triceratops research stems from various iconic discoveries. These finds have been pivotal in reconstructing the lifestyle and behaviors of Triceratops. For instance, the discovery of well-preserved skulls in North America has shed light on the distinctive horn formation and frill structure, allowing scientists to study these traits in detail. An example is the remarkably complete specimen found in Montana, which provided new insights into the growth patterns of these dinosaurs. Such discoveries are beneficial for establishing a clearer timeline of Triceratops' existence and evolution.
The key characteristic of these iconic fossil finds is their completeness, often yielding nearly intact skeletons. This allows researchers to conduct thorough examinations and comparisons. Unique features like the eye sockets or nostril patterns illuminate the evolution of these adaptations. However, while these iconic discoveries facilitate significant research, they can also offer misleading impressions if not contextualized correctly, potentially causing misconceptions about the life of Triceratops.
Exhibits in Museums
Exhibits in museums play a vital role in highlighting the grandeur of Triceratops within the larger discourse of paleontology. Museums curate impressive collections, showcasing meticulously assembled skeletons that are often the centerpiece of dinosaur exhibits. These displays not only engage the public but also inspire future generations of paleontologists and fossil enthusiasts.
The captivating visual nature of these exhibits is their key characteristic. They bring fossils to life, sparking curiosity and interest among visitors. Unique features, such as interactive displays or augmented reality elements, add a contemporary twist that enhances the educational experience. Nevertheless, while museum exhibits provide valuable insights into dinosaur biology and ecology, they may sometimes prioritize spectacle over scientific rigor, necessitating critical engagement from the audience.
Paleoecological Insights
Climate Change and Extinction
In examining climate change and extinction, we find a crucial aspect of Triceratops' paleoecological context. The late Cretaceous period, where these dinosaurs thrived, was marked by significant climatic shifts, influencing ecosystems and species survival. Understanding how Triceratops adapted—and ultimately succumbed—to these changes can shed light on the dynamics of extinction events.
The shifting climates of the time encapsulated the adaptive resilience of Triceratops. Focusing on these extinction events allows researchers to draw parallels with current biodiversity challenges. A unique feature of studying climate effects on Triceratops is recognizing that it wasn't just a single cause that led to extinction; rather, it was a culmination of environmental pressures. The advantage of this nuanced perspective is that it fosters a comprehensive understanding of life’s fragility under changing conditions.
Continued Research
Continued research into Triceratops fossils is indispensable as scientists strive to expand our understanding of dinosaur evolution. Ongoing excavations and technological advancements, like digital imaging techniques, allow researchers to uncover details previously thought lost. This aspect is particularly beneficial as it aligns with the increasing need for interdisciplinary approaches in paleontology, merging traditional methods with modern technology.
A key characteristic of continued research into Triceratops is its focus on interdisciplinary collaboration. For instance, partnerships between paleontologists and geologists enrich our understanding of sedimentary layers where fossils are found. This intersection of fields provides insights that are often overlooked. A unique advantage of ongoing studies is their potential to revolutionize our understanding of the Triceratops and its ecological interactions in the Cretaceous world. However, the disadvantage lies in the vast scale of research needed; critical findings may be slow to surface, demanding patience and persistence from the scientific community.
Evolutionary Relationships
Understanding the evolutionary relationships of Triceratops is crucial to grasp the broader context of its existence within the dinosaur lineage. The phylogenetic studies not only illuminate the family tree in which this remarkable creature belongs but also unravel the evolutionary adaptations that equipped it to thrive in its environment. Specifically, these relationships provide insights into how Triceratops, along with its relatives in the Ceratopsidae family, evolved various traits for survival, whether it’s their impressive horns or sprawling frills. This exploration paves the way for a deeper appreciation of the complexity of prehistoric life, opening doors to significant discoveries in the field of paleontology.
Phylogenetic Studies
Family Ceratopsidae
The Ceratopsidae family serves as a fascinating subject when examining evolutionary relationships. This family comprises horned dinosaurs, and it's characterized by their distinctive cranial frills and varying horn structures. Such unique traits are not merely for show; they hint at the adaptive strategies these animals employed to survive in the harsh conditions of the Late Cretaceous period. By studying the Ceratopsidae, researchers can trace back lineage characteristics that define not only Triceratops but also its relatives, such as Protoceratops and Styracosaurus.
A standout feature of the Ceratopsidae is their remarkable display of diversity in horn and frill formations, which is believed to play a significant role in social behavior, mating practices, and defense mechanisms. This makes the family a popular choice for research in evolutionary biology, drawing interest from various scientific circles and enthusiasts alike. However, challenges do exist when it comes to classifying these ancient creatures accurately, particularly as new fossils are uncovered and more data is available.


Comparative Morphology
Diving into comparative morphology reveals the physical structures and forms of Triceratops in relation to other ceratopsians. This area of study highlights the anatomy and morphology variations among species, pointing out functional adaptations which may have influenced their behavior and ecological roles. One key aspect of comparative morphology is the examination of skull shapes and size variations. The differing structures reveal a lot about their feeding habits and interactions with other species in the ecosystem.
Furthermore, comparative morphology allows scientists to deduce evolutionary directions taken by Triceratops and its relatives. This analysis sheds light on why certain species succeeded while others became extinct. The ongoing research in this field serves not only academic purposes but is also of substantial interest to collectors and enthusiasts who appreciate the intricate connections between form, function, and survival.
Speciation Events
Identification of Related Species
Identification of related species underlines the evolutionary pathways taken by Triceratops and its relatives. This aspect involves recognizing the fossilized remains that may share common ancestry, helping paleontologists paint a clearer picture of how these creatures diversified over time. A significant feature in this process is the discovery of new fossils that add to or challenge existing theories about relationships among dinosaurs.
The identification process often requires meticulous analysis of morphological characteristics, as well as ambient ecological factors that might have influenced speciation. The benefits of this approach are numerous; it not only enhances the understanding of Triceratops' position in the evolutionary timeline but also informs conservation efforts for current-day species by tracing back their ancestry.
Biogeographic Patterns
Examining biogeographic patterns yields valuable insights into how geographic distributions influenced the evolution of Triceratops and its kin. Patterns of ancient landforms and continental drift significantly impacted where these dinosaurs lived and how they adapted to diverse climates and ecosystems. A key characteristic of biogeographic studies is the ability to link fossil locations with environmental settings, providing context to fossil findings.
The unique feature of considering biogeography in studies is how it helps establish connections not only within species but across different families. This offers a clearer view of how climate and geographical changes led to adaptations or even extinctions, enriching the narrative of Triceratops and its relatives. Understanding these dynamics serves as a crucial aspect of paleontological research, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of life on Earth many millions of years ago.
Cultural Impact and Representation
The cultural portrayal of the Triceratops goes far beyond its physical attributes and fossil record. This dinosaur has become a potent symbol in various forms of artistic expression, playing a significant role in how society views prehistoric life. Through its depiction in art, literature, and popular media, we can stimulate discussions about evolution, extinction, and ecology. The importance of studying these cultural representations lies in their ability to shape public perception, inspire curiosity, and promote preservation efforts.
In Art and Literature
Fictional Depictions
Fictional representations of the Triceratops often embellish its distinct features, portraying it as a fierce protector and symbol of strength. For instance, many children’s books depict this dinosaur as a gentle giant, fostering a sense of wonder in young imaginations. This duality—both fearsome and friendly—allows people of all ages to connect with the creature on multiple levels. Such characteristics help make the Triceratops a popular choice for educational narratives, as it provides an opportunity to discuss the realities of herbivorous dinosaurs while captivating the reader's interest through storytelling.
From films to comic books, the Triceratops’ portrayal serves as a gateway for diving into themes of resilience and survival. Its unique feature—the prominent frill and horns—often symbolizes bravery, allowing narratives to deliver powerful messages about facing challenges, whether it’s in prehistoric landscapes or modern-day dilemmas.
Scientific Illustrations
When delving into scientific illustrations, the Triceratops has played an essential role in educating the public about prehistoric fauna. Illustrators strive to provide detailed representations based on fossil evidence, which serves to inform both specialists and the interested public about the dinosaur's anatomy, appearance, and behavior. This accuracy in scientific illustrations helps demystify the complexities of paleontological studies and bridges the gap between science and accessibility.
While convincing, these illustrations often come with their own set of challenges. Artistic interpretations risk oversimplifying or dramatizing features, leading to misconceptions about how these creatures lived. Nonetheless, they remain a focal point for fascination and inquiry, a means of igniting a lasting interest in paleontology that can engage and attract future researchers.
In Popular Media
Films and Documentaries
Films and documentaries have breathed life into the Triceratops, showcasing it in ways that combine education and entertainment. These media portrayals often emphasize the dramatic life of dinosaurs, including vivid reenactments of their environment and interactions. Notable examples, like Jurassic Park, have introduced the Triceratops to a broader audience, embedding it in the collective consciousness as a formidable part of the dinosaur world.
The characteristic of realism—melding actual scientific theory with compelling narratives—allows these films to inform as they entertain. However, downfalls may occur when the artistic liberties taken skew public understanding of dinosaur behavior, leading to stereotypes about their habits. Regardless, the dramatic presence of the Triceratops in such productions continues to stimulate interest in paleontology and the ancient world.
Toys and Merchandise
The wide variety of toys and merchandise featuring the Triceratops reflects its widespread appeal. From action figures to plush toys, these products not only entertain children but also educate them about this fascinating creature. The tactile and interactive aspects offered by toys enhance learning and encourage imagination, creating a lasting resonance with paleontological concepts.
Unique features of these products often include authenticity in design, which draws children closer to a standard of real-life dinosaurs. Nevertheless, while they can provide educational benefits, certain toys might inadvertently oversimplify traits, detracting from the complexities of the Triceratops’ behavior and lifestyle.
In sum, the cultural impact and representation of the Triceratops not just enrich our understanding of this dinosaur but also urge a fuller exploration of paleontology as a field. Each portrayal—whether in artistic expressions or popular media—contributes remarkably to the narrative of this unique creature, inviting rock and fossil collectors alike to appreciate its legacy.
The End
As we wrap up our exploration of the Triceratops, it's clear that this remarkable creature holds significant importance not only in paleontology but also in our understanding of Earth's history. Triceratops, with its distinctive physical characteristics and unique adaptations, has captivated the imagination of both scientists and enthusiasts alike. This final section sheds light on its legacy and examines future research directions that promise to enrich our knowledge of this iconic dinosaur.
The Legacy of Triceratops
Triceratops has left an indelible mark on the field of paleontology. Its fossil remains have contributed significantly to our understanding of the Cretaceous period's flora and fauna. The sheer size of its skull and the presence of its three horns often lead people to recognize it as one of the quintessential dinosaurs. Museums around the globe proudly display Triceratops skeletons, and these exhibits serve as a powerful reminder of the planet’s history during an era when these creatures roamed the earth.
The Triceratops has also become a cultural touchstone, appearing in various forms of media from documentaries to feature films. This popularity goes beyond entertainment; it plays a significant role in engaging the public's interest in paleontology. The narratives and visuals around Triceratops inspire the younger generations to explore the wonders of natural history, making them keepers of the legacy.
The study of Triceratops fossils offers insights that can shape our understanding of evolution, behavior, and adaptation in prehistoric ecosystems.
Future Directions in Research
Looking ahead, the field of paleontology is poised to delve deeper into the mysteries surrounding Triceratops. Advances in technology, such as high-resolution imaging and genetic analysis, could unravel complexities about its biology and behavior that we have yet to comprehend. Researchers are particularly interested in:
- Further Exploring Speciation: Identifying more closely related species could uncover the evolutionary pathways that led to the Triceratops's distinctive features.
- Habitat Analysis: Investigating geological data could reveal how climate variations affected their habitats and behaviors during the Cretaceous.
- Social Dynamics: Understanding better how Triceratops lived in herds or solitary could provide insights into their social structures and interactions with other species.
The ongoing study of Triceratops may also yield findings that impact broader fields such as ecology and climate science. With each discovery, we edge closer to understanding the intricate web of life that existed millions of years ago. The enduring allure of Triceratops ensures its prominent place in both scientific inquiry and public imagination
By delving into the past and bringing it into focus through research, we not only honor Triceratops's legacy but also push the boundaries of what we know about our ever-changing planet.



