Exploring the Diverse Applications of Malachite

Intro
Malachite is a unique mineral revered for its striking green hues and intricate banding patterns. This copper-based carbonate has been used throughout history for various purposes, transcending mere decoration. Its significance stretches from ancient civilizations to modern applications. Understanding its properties better can lead to greater appreciation, not just for collectors, but also for those involved in arts, health, and technology.
In this article, we will delve into diverse topics surrounding malachite. We will discuss its historical roles, identify its unique characteristics, and explore its applications across multiple sectors. By providing a comprehensive overview, the article aims to shed light on the multifaceted uses of malachite, inviting both enthusiasts and new collectors to engage with this remarkable mineral.
Foreword to Malachite
Malachite is a unique mineral with a rich history and diverse applications. This section serves as a foundation for understanding its significance in various cultural and practical contexts. As a vibrant green mineral, malachite draws attention not only for its aesthetic appeal but also for its numerous uses ranging from jewelry to healing practices.
Definition and Composition
Malachite is primarily composed of copper carbonate hydroxide, with a chemical formula of Cu2CO3(OH)2. Its distinct green color arises from the presence of copper within its structure, which can exhibit various shades of green depending on the mineral's formation. The formation processes include oxidation of copper ores and hydrothermal activity, making it commonly found in copper mining areas. This mineral has a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale, which makes it relatively soft compared to other gemstones. Its texture is often banded, leading to beautiful patterns that make it popular in decorative objects and jewelry.
Historical Context
Historically, malachite has held a place of importance in various cultures. Ancient Egyptians revered the mineral, using it for decorative items and as a cosmetic. They ground malachite to make eye paint that was believed to protect against evil spirits and enhance beauty. Additionally, malachite served as a valuable source of copper for the Phoenicians, who traded it extensively in antiquity. The mineral was also utilized in the artwork of various civilizations, with some artifacts dating back thousands of years still displaying malachite’s vibrant hues. Its use through the ages highlights not only its economic value but also its deep-seated cultural significance, connecting present-day enthusiasts to a long tradition of appreciation and functionality.
Malachite in Jewelry
Malachite has longstanding importance in the realm of jewelry, captivating artists and collectors for centuries. Its rich green color and unique banding patterns make it a sought-after gemstone for various jewelry pieces. Understanding its uses goes beyond mere aesthetics; it encompasses historical significance and modern design trends. Collectors often appreciate malachite not only for its beauty but also for its unique properties and meanings ascribed to it.
Traditional Craftsmanship
In ancient times, artisans skillfully worked with malachite, carving it into various shapes for decorative purposes. The Egyptians valued this stone as a protective amulet and used it in jewelry such as necklaces and rings. Malachite was ground into powder and used as eye makeup, demonstrating the mineral's multifaceted appeal.
The craftsmanship involved in creating malachite jewelry has evolved. Traditional methods included hand-carving and polishing, resulting in each piece being distinct. This craftsmanship connects deeply with cultural heritage, as various civilizations held malachite in high esteem due to its supposed protective and healing properties. Jewelers often incorporated intricate designs, reflecting the available motifs of the time, making the jewelry not just accessories but also statements of art and cultural identity.
Some notable techniques employed in traditional malachite jewelry include:
- Cabochon Cutting: A method that highlights the stone's natural beauty by polishing it into a rounded shape.
- Inlay Work: This technique involves embedding malachite into other materials, allowing for intricate patterns and designs.
- Filigree Work: Fine metalwork that beautifully complements the vibrant greens of malachite, typically seen in antique pieces.
Modern Jewelry Design
Today, modern jewelry designers continue to celebrate malachite, integrating it into contemporary aesthetics. The use of malachite is bold, serving to create statement pieces that attract attention. Designers often blend malachite with other gemstones and materials, crafting unique and innovative designs. There is a discernible trend towards sustainable practices as well, with some designers sourcing malachite ethically, reflecting a broader movement in the fashion industry.
Key attributes in modern jewelry design with malachite include:
- Minimalist Designs: Simple, elegant pieces that allow malachite's natural beauty to shine.
- Geometric Shapes: These styles highlight the stone's vibrant colors and patterns, appealing to modern tastes.
- Mixing Textures: Combining malachite with metals, ceramics, or woods to create depth and contrast in pieces.
The appeal of malachite in today's market is enhanced by its historical associations with vitality and protection. Each piece serves not just as a decorative item but as a conversation starter, linking wearers to the rich narratives that malachite embodies.
Healthcare Applications of Malachite
Malachite has drawn interest in diverse healthcare domains, particularly due to its purported healing properties. The role of malachite in health goes beyond aesthetics, merging traditional beliefs with modern perspectives. Individuals seeking alternative solutions often turn to malachite for various conditions, reflecting a broader trend toward holistic approaches in wellness.
Crystal Healing Practices
Within the realm of crystal healing, malachite holds a significant place. Proponents believe that touching or meditating with this mineral can facilitate emotional healing. Many practitioners suggest that malachite enhances transformation and deep healing. Its rich green hue is also thought to have calming effects on the mind.
Those who engage in crystal healing often use malachite to alleviate stress and anxiety. By placing malachite on the body or carrying it, some assert it can promote positivity and absorb negative energy. Reports claim beneficial impacts on physical ailments, especially those related to the heart and lungs. However, it is essential to understand that these claims are subjective and lack concrete scientific backing.
- Prominent Uses in Crystal Healing:
- Emotional healing
- Stress reduction
- Absorption of negative energies
Many are drawn to malachite not just for its beauty but also for its symbolic meanings in this context. It's advised, however, that one should not replace conventional medical treatment with crystal healing practices. Instead, it should be considered a complementary approach, if at all.


Scientific Perspectives
Examining malachite from a scientific viewpoint invites a different discourse. While there is limited empirical support for the claims surrounding malachite’s healing properties, studies on its mineral composition present interesting findings. Malachite contains copper and can release ions. Some researchers have explored the antibacterial properties associated with copper minerals. These elements are significant for those considering malachite in health applications.
Research surrounding malachite's benefits remains in preliminary stages. However, there is an acknowledgment of the need for further investigation. The focus shifts toward responsible use and sourcing to ensure safety. In this context, it’s crucial for users to distinguish between anecdotal experiences and scientific validation.
"The claims surrounding malachite's health benefits highlight a blend of ancient wisdom and modern skepticism. Jewelry and decorative items are popular, but future studies must clarify its role in health more rigorously."
In summary, malachite occupies a unique space in healthcare discussions. Whether in traditional healing practices or future scientific applications, its multifaceted nature invites exploration. Those interested in the mineral, especially rock and fossil collectors, can benefit from understanding both the cultural significance and the scientific scrutiny that it incites.
Malachite in Art and Decoration
Malachite has held a significant place in art and decoration throughout history. Its rich green hues, intricate patterns, and shiny surface appeal not just to artists but also to collectors and interior designers. In this section, we will explore historical artworks made from malachite, as well as its contemporary uses in interior design.
Historical Artworks
Malachite has been utilized in various forms of art for millennia. Ancient civilizations recognized its beauty and durability, choosing it for both its aesthetic and symbolic value. In ancient Egypt, malachite was often used to create ornaments, amulets, and even small statues. The stone was revered for its supposed protective qualities, and it adorned the tombs of pharaohs, serving as a connection to the afterlife.
During the Renaissance, malachite became popular among European artisans. It was carved into decorative objects, such as vases and table settings. Prominent figures, including Catherine the Great, commissioned malachite furnishings, exemplifying its status in high society. Notably, the Malachite Room in the Winter Palace of St. Petersburg represents one of the largest collections of malachite works, showcasing the stone’s vibrant color and intricate designs in a variety of applications.
"The use of malachite in art transcends aesthetics; it encapsulates cultural beliefs and history."
Contemporary Uses in Interior Design
In modern interior design, malachite continues to be a popular choice due to its visual impact. Designers often incorporate malachite into various elements, from wall panels to decorative accents. The stone's unique patterns can provide a touch of elegance and sophistication to spaces. Unlike traditional materials, malachite brings a natural element that can harmonize with both modern and classic decor.
Some notable applications include:
- Wall Art: Large slabs of malachite are used as statement pieces, enhancing spaces with rich textures and colors.
- Furniture: Coffee tables, side tables, and other furnishings crafted from malachite create focal points in living spaces, often surrounded by minimalistic decor to highlight their beauty.
- Accessories: Smaller items like coasters and vases bring a unique touch to home decor, allowing individuals to appreciate the stone daily.
The revival of interest in malachite aligns with contemporary trends emphasizing sustainable and natural materials in design. By choosing malachite, individuals connect with a rich heritage while embracing modern aesthetics.
Malachite in the Mineral Trade
The mineral trade is a vital aspect of the economic landscape associated with malachite. This section explores the importance of malachite in the market, its commercial value, and the ethical considerations tied to sourcing this enchanting stone.
Commercial Value
Malachite holds significant commercial value, driven by its unique aesthetics and cultural appeal. Its vibrant green color, striking patterns, and smooth finish make it a favorite among collectors and artisans alike. The mineral is often shaped into jewelry, decorative pieces, and even art, thereby enhancing its market demand.
- Price Variations: Prices for malachite can vary widely, dependent on several factors such as quality, size, and craftsmanship. High-quality pieces can fetch a premium, especially if they exhibit unique designs or historical significance.
- Market Demand: Demand for malachite remains strong, with its use in jewelry and home decor sustaining a steady interest. Modern consumers often seek unique materials that are both beautiful and meaningful, further boosting its allure.
- Investment Potential: Many collectors see malachite as not only a beautiful stone but also a wise investment. As rare specimens can appreciate over time, the mineral proves to be appealing in both aesthetic and financial terms.
Ethical Sourcing
Ethical sourcing of malachite plays a crucial role in the mineral trade. This subject has garnered attention as consumers become more aware of the implications tied to extraction. Advocating for responsible sourcing involves several key considerations:
- Origin Transparency: Buyers increasingly prefer clarity regarding the origin of the malachite. Ethical sourcing practices include detailed documentation that traces the mineral from its source to the final product.
- Environmental Stewardship: Sustainable mining practices are essential to minimizing the ecological impact associated with malachite extraction. This includes techniques that prevent habitat destruction and water pollution.
- Fair Labor Practices: Ensuring that workers involved in the extraction and processing of malachite are treated fairly and compensated adequately is vital for ethical considerations. Support for fair wages and safe working conditions contributes to a more sustainable trade.
"Consumers now seek more than beauty; they demand accountability in the materials they purchase."
Symbolism and Cultural Significance of Malachite
Malachite is more than just a striking green mineral; it carries rich meanings and significances across various cultures and time periods. Its historical context reflects a profound connection between nature's bounty and human belief systems. Understanding the symbolism of malachite can deepen appreciation for its aesthetic and practical uses.
The cultural significance of malachite extends to its associations with protection, transformation, and prosperity. Many ancient civilizations revered the stone, attributing powerful qualities to it. The idea that stones could hold protective energies or manifest intentions demonstrates the interplay between physical matter and metaphysical beliefs.
Cultural Beliefs
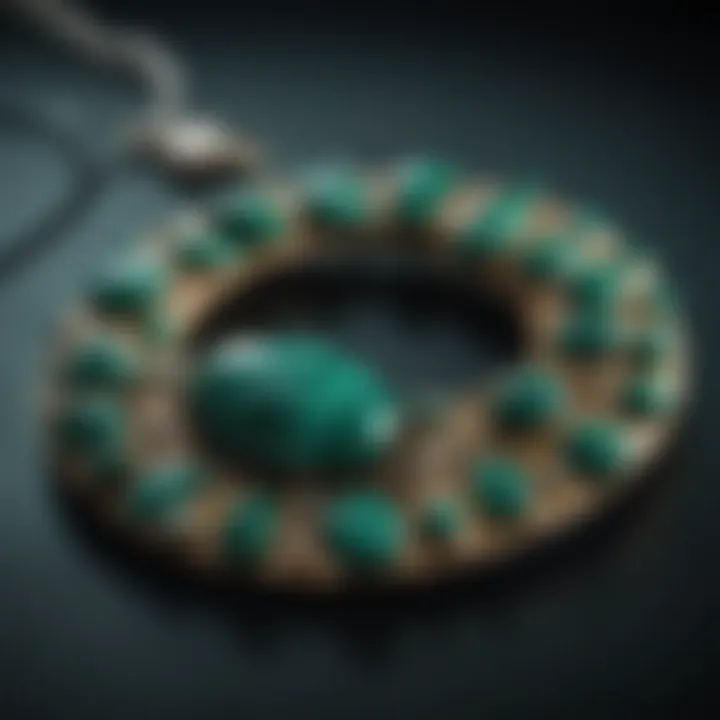


Many cultures have complex beliefs surrounding malachite. In ancient Egypt, the stone was seen as a protective talisman. It was often used in burial artifacts, believed to guard the deceased from negative energies in the afterlife. The Egyptians also associated malachite with the goddess Hathor, representing beauty, love, and celebration.
In Russia, malachite has been a symbol of wealth, extensively used as a decorative stone in palaces and churches. The Malachite Room in the Winter Palace of St. Petersburg showcases the stone's luxurious appeal.
Throughout history, the use of malachite in jewelry and talismans speaks to its perceived spiritual significance. Many believe it can absorb negative energies and transform them into positive vibrations. People often wear malachite for emotional healing, considering it to promote harmony and balance in relationships. The beliefs indicate a fragile balance between aesthetic appreciation and the yearning for emotional security.
Malachite in Folklore
Folklore offers rich narratives surrounding the use and characteristics of malachite. In various traditions, the stone is said to protect the wearer from danger, particularly in the form of physical accidents or illness. It is often referred to as a stone of transformation, suggesting its potential to bring growth and change in one's life.
Many cultures tell stories of how malachite can be harnessed for divination purposes. Individuals might use pieces of malachite in rituals to connect with the spirit world or tap into knowledge beyond their understanding. It's seen as a path toward enlightenment, guiding individuals through introspection and reflection.
"Malachite's colors are a reminder of nature's cycles, symbolizing rebirth and renewal. It encourages individuals to face changes with resilience and courage."
In modern contexts, these perspectives persist, resonating strongly with individuals seeking personal growth and healing. Whether displayed as art or worn in jewelry, malachite continues to inspire conversations about its rich cultural roots and myriad meanings.
Educational Uses of Malachite
The role of malachite in education is both fascinating and significant. This mineral not only enriches geological studies but also serves as an important teaching tool in natural history. Its unique properties and striking appearance make it an engaging subject for learners of all ages. Educators and students benefit from studying malachite, as it enhances their understanding of geology, crystal structures, and the earth's mineral resources.
Geological Studies
Malachite is a valuable mineral for geological studies. It is classified as a carbonate mineral and primarily consists of copper carbonate hydroxide. The green color of malachite comes from copper ions that are present in its structure. The mineral is often found in the oxidized zones of copper deposits, making it a key indicator for geologists studying mineralogical formations.
Studying malachite can provide insights into:
- Mineral Formation Processes: Malachite often forms from the weathering of copper ores. This may include insights on how existing minerals break down and change forms.
- Geological Mapping: Its distinct color aids in distinguishing different geological layers and formations. This helps researchers in mapping the distribution of copper and associated minerals.
- Environmental Understanding: Understanding how malachite forms tells researchers about the local environment and its history. This includes factors such as temperature, pH levels, and the presence of other minerals.
Teaching Materials in Natural History
In natural history, malachite is often used as a teaching material to illustrate various geological concepts. Its striking visual properties and historical context make it an excellent educational tool. Teachers can prepare lessons on the following:
- Rock Cycle: Malachite can exemplify processes in the rock cycle, illustrating how minerals transform from one type to another over time.
- Mineralogy: Students can learn about crystallography by examining the unique crystal structures that malachite possesses, which includes its fibrous appearance.
- Cultural and Historical Context: Focusing on malachite’s significance in ancient cultures can enhance students' understanding of the interplay between society and mineral resources.
Malachite can be used in various formats, such as:
- Mineral Exhibits: Using malachite specimens in museum displays enriches visitors' experiences and knowledge.
- Laboratory Experiments: Practical lab work can involve students examining the physical properties of malachite, fostering analytical skills and scientific inquiry.
- Curriculum Integration: Malachite can be integrated into broader curriculum themes like sustainability and resource management. By discussing mining practices and ethical sourcing, educators can provide a well-rounded perspective on mineral resources.
"Studying malachite not only broadens students' understanding of geology but also connects them to the historical significance of this captivating mineral."
Through these educational uses, malachite remains more than just a mineral; it is a gateway to a deeper appreciation and understanding of Earth sciences.
Environmental Considerations
Understanding the environmental considerations associated with malachite is crucial. This section explores sustainability practices and the impact of malachite mining on ecosystems. Given the growing concern about environmental degradation and the demand for responsible sourcing, it becomes imperative to assess and implement sustainable methods in the malachite trade. Without attention to these issues, the allure of malachite can come at a hefty ecological cost.
Sustainability Practices
Sustainability practices have gained importance in recent years, especially in mineral sourcing. When it comes to malachite, this is no different. Ethical mining practices ensure that the extraction of malachite does not compromise the integrity of surrounding environments. Some of the key sustainability practices in malachite sourcing include:
- Responsible Mining: This involves limiting the ecological footprint by using techniques that minimize land disruption. Methods like selective mining reduce waste and protect biodiversity.
- Reclamation Efforts: After mining is complete, reclamation is vital. This process involves restoring land to its natural state or repurposing it for sustainable use.
- Community Engagement: Engaging local communities in the mining process ensures that their needs are considered. It helps to create a framework where both companies and communities can benefit.
By adhering to these practices, the malachite industry can help ensure that it preserves the environment for future generations while still meeting market demands.
Impact on Ecosystems
The impact of malachite mining on ecosystems cannot be underestimated. Mining operations can lead to habitat destruction, soil degradation, and water pollution if not managed correctly. Some of the notable environmental impacts include:
- Habitat Loss: Mining activities often involve clearing large areas of land, which destroys the habitats of various species. This loss of biodiversity is a significant concern for environmentalists.
- Water Pollution: The extraction process might lead to the leaching of harmful substances into local waterways. Such pollution affects not only aquatic life but also the overall ecosystem health.
- Soil Erosion: When land is stripped of vegetation for extraction, it becomes vulnerable to erosion. This can lead to sediment runoff into water bodies, further degrading water quality.
Mitigating these impacts requires conscientious planning and adherence to environmental regulations. Responsible mining companies are actively seeking to balance the benefits of malachite extraction with the needs of the ecosystem.
"The true value of a mineral lies not only in its market price but also in its relationship with the environment."
By focusing on these aspects, stakeholders can work towards a future where malachite is sourced sustainably, contributing to both economic growth and ecological balance.
Malachite in Technology
Malachite's integration into technological sectors marks a significant evolution in how minerals can contribute beyond decorative purposes. This section delves into malachite’s role in industrial applications and emerging innovations, highlighting its versatility and the potential advantages it offers.
Industrial Applications
In industry, malachite finds its most prominent application in the production of copper. Historically, it served as a crucial ore for acquiring copper due to its high copper content, thus spurring technological advancements around metallurgy. As an economic resource, malachite contributes to various manufacturing processes, particularly in electrical components and plumbing materials.
The extraction of malachite for copper also opens opportunities for recycling and sustainability efforts. With rising interest in eco-friendly practices, industries leverage malachite’s natural properties to create less toxic alternatives in manufacturing, particularly in the creation of paints, pigments, and dyes.
Key points of industrial applications include:
- Copper extraction: Essential for producing electrical wiring and components.
- Sustainable alternatives: Demand for environmentally friendly paints and dyes drives interest in malachite derivatives.
- Metallurgical advancements: Ongoing research into malachite's extraction processes enhances efficiency.
Emerging Innovations
Recent technological advancements have led to innovative uses of malachite that may redefine its applications in multiple fields. One such emerging area is its utilization in renewable energy applications. Malachite's unique mineral properties lend themselves well to the development of new types of batteries and energy storage solutions. As the global demand for efficient energy storage grows, malachite could provide a feasible and less harmful resource compared to traditional materials used in battery technology.
Moreover, there is an increasing focus on malachite in the realm of nanotechnology. Researchers are exploring its potential for creating new nanomaterials that may enhance various technological applications such as sensors and catalysts. These discoveries could lead to breakthroughs in efficient chemical reactions and environmental monitoring systems.
"Malachite's unique properties and versatility make it a prime candidate for innovative technological applications, pushing the boundaries of traditional uses."
In summary, malachite's role in technology reflects a blend of historical significance and potential future development. Its applications span critical industrial uses to pioneering innovations that may impact renewable energy and advanced materials. Understanding and exploring these connections emphasizes the importance of malachite in contemporary technological landscapes.
Care and Preservation of Malachite
When considering the harmonious relationship between the collector and their malachite specimens, care and preservation become fundamental. Malachite is a vibrant mineral that captivates with its rich green color and unique patterns, yet it is also relatively delicate. Thus, understanding the importance of its upkeep is critical. Proper care extends the life of the specimen, ensuring its visual appeal and structural integrity for generations. Furthermore, collector’s value can significantly appreciate if the malachite is well-maintained, drawing attention from connoisseurs.
Cleaning Techniques
Cleaning malachite can be meticulous. The mineral is susceptible to harsh chemicals and abrasives, so it is vital to use gentle methods.
- Soft Cloth: Using a soft, lint-free cloth can effectively remove dust and fingerprints without scratching the surface.
- Mild Soap Solution: For deeper cleaning, a solution of warm water and mild soap can be employed. Dampen the cloth, never soak the malachite, and gently wipe the surface. Heavy scrubbing should be avoided.
- Avoid Water and Heat: Prolonged exposure to water may weaken the mineral. Thus, it should be kept dry. Additionally, do not expose it to direct sunlight or heat sources, as temperature fluctuations can cause cracks.
To ensure malachite remains striking, routine cleaning every few months is advisable. This will keep its vibrant color intact.
Long-Term Storage Considerations
When it comes to storing malachite, attention to environmental factors is paramount. Improper storage can lead to damage, dullness, and even irreversible changes.
- Storage Location: Keep malachite away from areas with high humidity, as moisture can cause oxidation. A climate-controlled environment is ideal.
- Separate from Other Minerals: Store malachite separately from other minerals to prevent scratching. Using a padded box or a display case with compartments is a sound strategy.
- Avoid Chemicals: Ensure that no household chemicals or perfumes are kept near the storage area. These substances can inadvertently damage the surface of the crystal.
- Regular Checks: Periodically inspect the stored specimens for any signs of deterioration. Early detection can prevent significant damage, preserving both appearance and value.
Finale
The importance of the conclusion in this article lies in its ability to encapsulate the wide-ranging uses and benefits of malachite, a mineral revered for its beauty and utility. Through a detailed exploration of malachite’s properties and applications across various sectors, we have established its relevance not only in art and jewelry but also in health, technology, and environmental sustainability. Understanding these facets underscores the mineral's significance beyond aesthetics.
Recap of Malachite's Versatility
Malachite showcases a remarkable versatility that is both ancient and modern. From its historical usages in decorative arts to contemporary applications in healing and technology, the mineral serves various needs across multiple platforms. Notably, cultural significance punctuates its value. Rock and fossil collectors should appreciate the exploration of its varied dimensions:
- Historical Use in Jewelry: Traditional craftsmanship has celebrated malachite for centuries, making it a sought-after gemstone.
- Healthcare Applications: Many believe in its therapeutic benefits, drawing interest from holistic health communities.
- Industrial Applications: Malachite finds its way into various technologies, enhancing product design and functionality.
- Environmental Impact: Ethical sourcing practices draw attention to sustainable methodologies regarding its acquisition.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, the future of malachite is poised for further exploration and innovation. Several trends are emerging:
- Sustainable Practices: As environmental awareness grows, the demand for ethically sourced minerals, including malachite, will likely increase.
- Technological Integration: New applications in technology could lead to novel methods of utilizing malachite, perhaps in advanced materials or eco-friendly products.
- Expanded Gemstone Market: As collectors’ interests expand, malachite may see heightened demand in markets focusing on unique and rare gemstones.
- Educational Initiatives: Increasing interest in geology and mineralogy will potentially spark a resurgence in educational materials utilizing malachite.



