Exploring Utah's Remarkable Dinosaur Fossils


Intro
Utah has long captured the curiosity of scientists and fossil enthusiasts alike. The state is a veritable goldmine when it comes to dinosaur fossils. With its varied landscapes and stratified rock formations, Utah provides an array of environments where these ancient creatures once roamed. From the arid deserts to the lush river valleys, it offers a unique glimpse into the past.
The legacy of dinosaur fossils in Utah is not only about the finds themselves; it encapsulates a broader narrative about the earth’s history and how life evolved over millions of years. Significant fossil discoveries like the Allosaurus and the sauropod dinosaurs have effectively reshaped our understanding of the Mesozoic Era. These findings have consequences that stretch beyond just the scientific community by igniting the imaginations of the general public and preserving our planet's rich history.
In this exhaustive piece, we will explore everything from the major fossil sites, like the Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry, to the myriad excavation methods that paleontologists use. We’ll also dig into the historical significance of these discoveries, providing insights into how they not only enhance our scientific understanding but also create opportunities for collectors and researchers alike.
Intro to Dinosaur Fossils
Dinosaur fossils hold an integral place in the tapestry of Earth's history, particularly when exploring regions like Utah, which is known for its rich paleontological resources. Understanding these fossils is not merely about the bones and teeth that have been preserved in the Earth’s crust; it encompasses a broader narrative about the ancient ecosystems and the evolution of life on our planet. This introduction serves as a springboard into the vast intricacies of dinosaur fossils, highlighting their significance, the reasons our understanding of them matters, and the sheer excitement they spark in collectors and scientists alike.
Definition and Importance
At its core, a dinosaur fossil is the preserved remnant or trace of a dinosaur, be it bones, footprints, or even skin impressions. These remnants are crucial for paleontologists as they piece together the enigmatic story of life millions of years ago. Each fossil unearthed can reveal information about how dinosaurs lived, what they ate, and even how they interacted within their ecosystems.
Moreover, the importance of dinosaur fossils goes beyond just scientific inquiry. They serve as tangible evidence of an ancient world that once thrived, drawing enthusiasts and researchers to Utah, where many notable fossils have been discovered. The stories behind these fossils not only provide glorious insights into our planet's past but also inspire questions about evolution, extinction, and the adaptability of life.
Overview of Dinosaur Fossil Discoveries
The exploration of dinosaur fossils has a storied history that reveals the evolution of paleontological methods and theories over time. From the early discoveries in the 19th century, when the first dinosaur bones were identified, to the high-tech excavations of today, each significant find transforms our understanding of these magnificent creatures.
Key areas in Utah, such as the Morrison Formation, have been focal points for fossil discoveries. This well-known formation has yielded a plethora of dinosaur bones, as well as images of prehistoric environments. The various species found—including large theropods and the armored stegosaurus—paint a vivid picture of the diversity in dinosaur life and the habitats they occupied.
In essence, the ongoing research and discoveries in Utah not only advance academic understanding but also fuel public interest, encouraging educational outreach regarding ancient life and the importance of conservation efforts for our delicate ecosystems today.
Ultimately, as we delve further into this article, the reader will gain a more profound appreciation for the role dinosaur fossils play—not only in the realm of paleontology but as a bridge connecting us to history.
Utah's Geological Significance
Utah stands out not just for its awe-inspiring landscapes but also for its rich geological tapestry. The state's geological significance is woven tightly into the study of dinosaur fossils, providing a unique vantage point into the Earth's history. The layers of rock found here have witnessed the rise and falls of various species, allowing paleontologists to piece together a clearer picture of life during the Mesozoic Era. Utah’s geological formations are like open books revealing ancient tales, each stratum offering clues about the ecosystems that existed millions of years ago.
Geological Layers and Timeframes
The geological layers in Utah are an essential aspect when examining the timeline of dinosaur existence. These strata reflect different epochs during which dinosaurs thrived, with each layer corresponding to specific timeframes. The sediments deposited over millions of years create a mosaic of geological history that illustrates changes in climate and environment.
For instance, the Cretaceous layer, where many significant fossils have been found, dates back approximately 145 to 66 million years ago. This timeframe is fundamental as it marks the latter part of the Age of Dinosaurs. The geological assessments performed by researchers reveal insights into how these ecosystems evolved over eons, not just in terms of fauna but also flora, which was crucial for supporting these massive creatures.
Key Geological Formations
Rocky Mountain Formation
The Rocky Mountain Formation is a cornerstone of Utah's geology, known for its towering peaks and rich fossil beds. This formation is primarily composed of sedimentary rocks that record a significant stretch of the Earth’s history. The prevailing characteristic of the Rocky Mountain Formation is its impressive vertical elevation, which gives insights into the tectonic activities that shaped the region.
One of the unique features of this formation is the variety of fossils it hosts. From sea creatures to terrestrial dinosaurs, the array of fossils found here speaks volumes about the diverse environments that have existed over time. This formation underscores the importance of tectonics in fossil preservation and shows how ancient landscapes can both benefit and challenge fossil hunters.
Morrison Formation
In contrast, the Morrison Formation is often referred to as the Holy Grail of dinosaur fossils. This formation is renowned for yielding an impressive variety of dinosaur remains, including famous species like Brontosaurus and Apatosaurus. The Morrison Formation showcases a characteristic clay-rich matrix, providing optimal conditions for the preservation of fossils. It stands out as a
Major Dinosaur Fossil Sites in Utah
Utah stands as a treasure trove for paleontologists, with its diverse dinosaur fossil sites nourishing both the scientific community and enthusiastic collectors alike. This rich array not only offers insights into the behaviors and habitats of these ancient creatures but also serves as a bridge linking the past to our present understandings of evolution. Today, we explore some of Utah's top fossil sites: Dinosaur National Monument, Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry, and the Utah Field House of Natural History.
Dinosaur National Monument
Historical Perspectives
Dinosaur National Monument, established in 1915, has been a prominent site for fossil discovery. The history of this monument is marked not only by its geological significance but also by its role in the evolution of public interest in paleontology. This site became famous in the 1950s due to the uncovering of a massive quarry of dinosaur bones, which was so extensive that the bones were still set in the surrounding rock.
One of its key characteristics is its dedication to preserving the fossils in situ, allowing visitors a glimpse into the original excavation process. This unique aspect highlights the significance of context in paleontological studies. By being able to see the bones in their natural environment, the value of this perspective is truly appreciated, as it fosters a deeper understanding of the ecosystems that once existed.
Visitor Insights
Visitor engagement at Dinosaur National Monument is highly interactive, enhancing the overarching narrative about dinosaurs. Many visitors come to witness not only the fossils but also the stunning landscapes that frame the exhibits. Guided tours, talks, and visitor centers provide educational experiences that are both informative and accessible to diverse audiences.
The unique feature of this site is that it intertwines education and adventure. Families can enjoy picnics while soaking in the prehistoric history surrounding them. However, one disadvantage may be the high foot traffic during peak seasons, which could lead to a less focused experience in certain areas.
Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry
Excavation History
The Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry boasts an excavation history that traverses nearly a century, with initial discoveries tracing back to the 1920s. Over 12,000 dinosaur bones have been excavated from this site, marking it as a hotspot for researchers. One of the remarkable aspects of this quarry is its identification of a concentrated layer of bones, as if a catastrophic event led to many dinosaurs meeting their demise there at once.
This reinforces Cleveland-Lloyd's repute as a public interest site, fascinating those who ponder the events that unfolded during that time. The unique feature of the quarry is its ongoing excavation; even though it has been extensively worked over decades, researchers still unearth new finds that contribute to the understanding of the Jurassic period.
Species Discoveries
Cleveland-Lloyd has been credited with the discovery of numerous species, including Allosaurus and Stegosaurus, making it highly significant to the field of paleontology. Each discovery adds a layer to the tapestry of our understanding of dinosaur diversity in North America. What elevates this quarry further is how it has become a case study in predator-prey dynamics among dinosaurs.
The identification of high numbers of carnivorous dinosaurs relative to herbivores raises important questions regarding the ecological balance of the time. While the quarry successfully sheds light on various dinosaur species, it also faces criticism for the lack of detailed species data, which some argue limits comprehensive research into growth and development of various dinosaur kind.
Utah Field House of Natural History
Exhibits Overview
The Utah Field House of Natural History offers an impressive exhibit array showcasing the diverse prehistoric life once found in the region. A key feature of the Field House is its commitment to making paleontology relatable and engaging. With life-size dinosaur models and interactive displays, it encapsulates an educational experience that lingers long after visitors leave.
The overwhelming aspect of these exhibits is how they present both fossils and casts, allowing for a tangible connection to the past. Visitors can see fossils amid reconstructions of ecosystems that existed millions of years ago, offering a holistic view of life during the Mesozoic Era. However, while exhibits are plentiful, some critiques focus on the need for continuous updates to reflect new discoveries.
Educational Programs
The educational programs provided by the Utah Field House stand out as a beacon for community engagement. Programs are designed to ignite interest not only in paleontology but also in science as a whole. Workshops, children’s camps, and lectures feature prominently, drawing in educators and families alike.
Unique programs tailored for young ones aim to build curiosity about geology and biology through hands-on experiments and fossils handling. However, challenges arise in securing funding to maintain and expand these educational initiatives, impacting the breadth of offerings.
"By understanding our prehistoric past, we can better appreciate the complexities of life, evolution, and terrestrial ecosystems today."
Notable Dinosaur Discoveries
Dinosaur fossils are often the keys to unlocking secrets of the past. Within Utah’s vast landscape, these notable discoveries offer insights that aid in understanding not just the creatures themselves, but also the ecosystems and environments where they thrived. Each find serves as a puzzle piece that contributes to the broader narrative of our planet’s prehistoric life. Understanding these discoveries isn't merely an academic exercise; it helps connect us with millions of years of biological heritage. Let’s take a closer look at some of these famous finds.
Famous Finds
Allosaurus
The Allosaurus is regarded as one of the more well-known theropods found within Utah, standing out due to its impressive size and predatory nature. This dinosaur, often depicted as a formidable predator, provides crucial insights into the hunting behaviors and ecological dynamics of the Late Jurassic period. Dave's Creek Canyon, a well-recognized area, is known for yielding distinct Allosaurus fossils, which enable researchers to piece together its diet and interactions.
A key characteristic of Allosaurus is its unique skeletal structure; it possesses large, sharp teeth and powerful limbs, which were likely advantageous for tackling larger prey. The discovery of these fossils is particularly beneficial for paleontologists interested in therapod evolution and behavior, enriching our understanding of carnivorous dinosaurs.
"Allosaurus fossils have revolutionized the understanding of predator-prey relations during its time, highlighting its significant role in the ecosystem."
However, the major takeaway is its unique adaptations that underscore its place in the dinosaur lineage, yet often leaves discussions about its potential competitors and threats to speculation.
Stegosaurus
The Stegosaurus, another stalwart of dinosaur fame, is easily distinguished by its plate-covered back and spiked tail. These physical traits prompt intriguing questions about behavior and defense mechanisms against predators. Numerous Stegosaurus fossils have been unearthed in Utah, particularly within the Morrison Formation, further enriching the fossil record.
One of the most fascinating aspects of this dinosaur is its presumed ability to regulate body temperature through those large plates. This kind of thermal regulation poses important questions about the life habits of these massive herbivores. Stegosaurus serves as a significant example because studying its fossils aids researchers in viewing the complexities of diet and environment during the late Jurassic. Yet, while the plates provide a striking image, some argue that they're a distraction from exploring its more subtle anatomical advantages.
Utahraptor
When we shift our focus to Utahraptor, which roamed the Earth during the Early Cretaceous, we encounter a raptor that melds both strength and agility. This dinosaur, which is notably larger than its Jurassic counterparts, offers a fascinating glimpse into the evolution of predatory strategies among dinosaurs. Fossils of Utahraptor are foundational in understanding the family's developments in speed and hunting proficiency.
Utahraptor’s robust build and innovative hunting tactics contribute to its allure as a specimen for study. It also highlights the predator-prey dynamics unique to its era. With its impressive claws and potential pack-hunting behavior, Utahraptor represents a shift in how the predatory models of dinosaurs might have looked. Yet, its size sometimes overshadows its anatomical complexity, which could reveal more about how it interacted with both prey and competitors.
Impacts on Paleontology
Each notable discovery not only showcases the unique characteristics of specific dinosaurs but also plays a role in advancing the field of paleontology. They help shape research priorities, influence museum exhibitions, and contribute to educational narratives that captivate both scientists and the public alike. Key insights drawn from these fossils lay the groundwork for future explorations and scaffold the critical inquiries that drive the scientific community forward.
Understanding these findings sheds light on evolutionary pathways and inter-species interactions, ultimately enriching our collective knowledge of prehistoric life. As researchers continue to study these fossils, they’re not only delving into the past but also framing how we understand ecological narratives today.
Methods of Excavation and Preservation
The methods of excavation and preservation are critical components in the field of paleontology. Understanding these processes is not just about digging up bones; it's about safeguarding a piece of history. In Utah, where the land is rich with dinosaur fossils, these methods allow researchers to uncover and retain invaluable information about the Mesozoic era. This section discusses excavation techniques and preservation methods, emphasizing their significance in ensuring the integrity and longevity of fossil specimens.
Excavation Techniques
Excavation techniques refer to the procedures and tools utilized to carefully extract fossils from their resting places in the rocky layers of the Earth. These techniques can vary widely, which is largely dependent on factors like the type of site, the nature of the fossils, and the surrounding geological conditions.
One primary technique involves the use of hand tools like brushes, chisels, and picks to meticulously remove layers of earth without damaging the fossils. This method requires a delicate touch, reflecting the importance of patience and attention to detail.
In some instances, heavier machinery may be employed, particularly in larger quarries where extensive fossil beds exist. However, this method brings its own challenges. If not handled correctly, the potential for damage to fossils increases significantly. Researchers often adopt a hybrid approach where initial ground removal is done through machinery, followed by finer excavation with hand tools.
Preservation Methods
Once fossils have been excavated, careful preservation techniques are essential to maintain their condition for future study and display.
Polymer Applications
Polymer applications have emerged as a mainstay in fossil preservation due to their versatility and effectiveness. These synthetic substances can be applied as consolidants, helping to stabilize and protect fragile specimens. The key characteristic of polymer applications is their ability to create a strong yet flexible bond with both organic and inorganic materials.
One of the most beneficial aspects of using polymers is that they can penetrate deep into the structure of fossils, ensuring that even the most delicate pieces receive adequate protection. However, while polymers are excellent for short-term enhancements, they often require careful monitoring in the long term due to potential chemical interactions as they age.
Field Techniques
Field techniques encompass a range of strategies applied during the excavation process to ensure that fossils remain intact until they can be transferred to a lab for further analysis. These methods often include the wrapping of specimens in protective materials like gauze or burlap bonded with plaster to form casts. This not only guards against physical damage but also helps to retain the fossils' original context, which can provide valuable information during analysis.
A unique feature of field techniques is their adaptability; depending on the fossil's size, condition, and location, techniques can be modified to maximize protection. However, these methods rely heavily on skilled personnel who can carry out the necessary procedures effectively. A lack of experience in applying these techniques can lead to mistakes that might compromise the integrity of the fossils.
The combination of effective excavation and preservation methods truly allows paleontologists to advance our understanding of ancient life, safeguarding these incredible remnants of the past for future generations.
These methods not only enhance the preservation of significant fossil finds but also contribute significantly to ongoing research projects, educational programs, and public engagement activities.
Paleontological Research in Utah
The landscape of Utah is not just a stunning vista; it holds secrets buried deep within its geological layers. Paleontological research in Utah is crucial, as it helps to unravel the ancient history of life on Earth. The state's diverse ecosystems during the Mesozoic Era are preserved in its rock formations, providing invaluable insights into the evolution of dinosaurs and other prehistoric creatures.
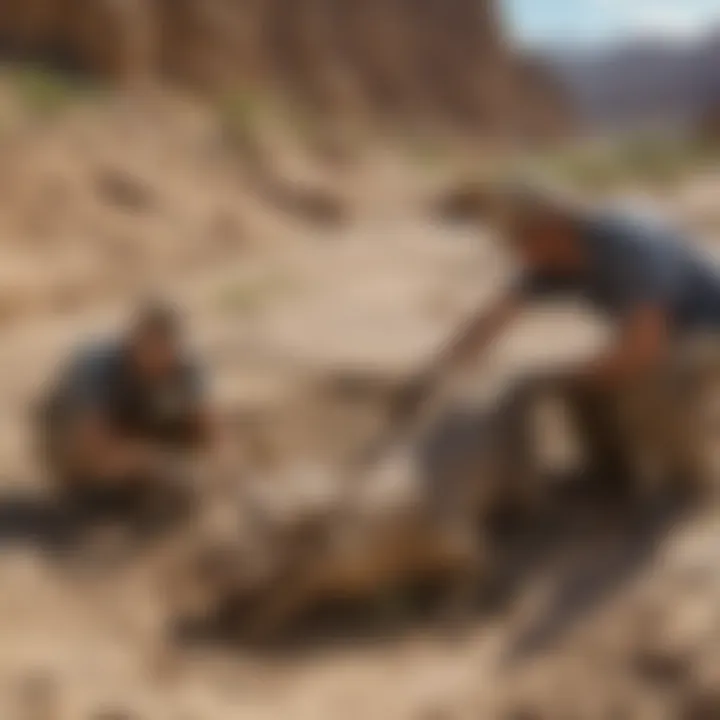


Significance of Research
Research in this realm isn't merely academic—it's about piecing together the story of our planet. Through various studies, paleontologists gather evidence that informs not only our understanding of dinosaurs but also broader ecological and evolutionary patterns. Utah stands out for its rich fossil beds, making it a hub of activity for scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Research Institutions
Utah is home to several prestigious research institutions that play a pivotal role in advancing paleontological knowledge. Institutions such as the Natural History Museum of Utah and the Utah Field House of Natural History provide essential resources and expertise. These organizations not only house significant fossil collections but also facilitate research projects that attract scholars from around the globe.
The collaboration between institutions and universities across Utah enhances the academic community's ability to conduct comprehensive studies. This cooperative environment fosters innovation and encourages the dissemination of new findings, thereby enriching our understanding of dinosaur lineages.
Institutions at a glance:
- Natural History Museum of Utah
- Utah Field House of Natural History
- Brigham Young University
- University of Utah
These entities support vibrant research programs and offer educational outreach that cultivates a deeper interest among the public.
Current Studies
Currently, paleontological research in Utah is thriving, with various projects underway focusing on different aspects of the Mesozoic ecosystem. Researchers are employing cutting-edge techniques, such as scanning technology, to analyze fossils without damaging them. This non-invasive approach is invaluable for preserving the integrity of specimens.
Moreover, studies in fossil preparation and analysis are being conducted to address pressing questions about dinosaur behavior, diet, and evolutionary adaptations. For instance, recent research has explored the herbivory patterns of certain dinosaur species, adding a layer of understanding to their ecological roles.
*"The more we explore, the more we find fascinating connections between ancient and modern ecosystems," notes Dr. Jane Smith, a leading paleontologist at the Natural History Museum of Utah.
As researchers delve into current studies, they're not just unearthing bones; they’re unearthing stories that link prehistoric life to present-day species. This ongoing investigation keeps expanding the body of knowledge, shedding light on how life has evolved in response to environmental changes over millions of years.
The Role of Fossils in Understanding Evolution
The study of fossils reveals a great deal about the past, particularly in understanding evolution. Fossils serve as time capsules, giving us a glimpse into life forms that roamed the Earth eons ago. In this era where technology and biology often intersect, fossils remain a crucial link. What's interesting is how these relics of the past can shed light on the journey of species as they adapt and evolve in response to changing environments. Fossils aren't just remains; they are records of existence that tell the story of a world we can hardly begin to imagine.
Insights into Mesozoic Ecosystems
Diving deeper into the Mesozoic Era, which is often dubbed the Age of Reptiles, we find that fossils play a large role in re-creating an ecosystem that shaped the planet’s biological heritage. By examining the fossilized remains of dinosaurs and other creatures, scientists can construct a picture of how these animals lived, hunted, and interacted with their surroundings.
For example, the rocks in Utah contain evidence of diverse habitats, ranging from arid environments to lush, green valleys. Fossils reveal not only the dinosaurs but also the smaller creatures that coexisted with them. Pollen grains found in sedimentary layers can inform us about the types of plants that thrived, while footprints can reveal social dynamics, like whether certain species roamed in packs or alone.
Additionally, many fossils provide insights into predator-prey relationships. For instance, the presence of large theropods alongside smaller herbivores suggests a complex food web. This can help modern scientists draw parallels with today’s ecosystems, highlighting how interspecies relationships may develop over time.
Connecting Past to Present
Connecting the dots between the fossil record and today’s biological diversity is not simply an academic endeavor but a vital part of understanding how life has evolved. This connection ultimately enriches our comprehension of current species and ecosystems.
One significant aspect is the concept of evolutionary adaptations. For instance, fossils show us how dinosaurs adapted their morphology to meet the demands of their environment—think of the long neck of a Brachiosaurus, perfectly suited for browsing high vegetation. This adaptation sheds light on contemporary animals facing similar adaptations due to climate change and habitat loss.
Moreover, paleontological research increasingly emphasizes the importance of species extinction and survival. Studying mass extinction events, like the one that wiped out the dinosaurs, can offer valuable lessons for understanding current biodiversity crises. The extinction of species and the subsequent rise of new forms teach us about resilience and the potential for recovery in today’s ecosystems.
Ultimately, fossils irrefutably demonstrate that the past is intertwined with the present. By piecing together these ancient tales, we gain richer insights into the mechanisms and pathways of evolution that have led to the world we know today.
"Fossils are more than mere remnants of life; they are essential clues unlocking the mysteries of evolution, connecting ancient ecosystems with the vibrant web of life we see today."
Through careful research and dedicated study of fossils in Utah and beyond, we stand a better chance of navigating life's future challenges every bit as much as we strive to understand its past.
Collecting and Caring for Fossils
Collecting and caring for fossils is more than just a hobby; it is an essential practice that enhances both personal understanding and the broader scientific community's knowledge. For paleontologists and enthusiasts alike, fossils serve as time capsules, providing a window into life millions of years ago. In the specific context of Utah, a state rich in dinosaur remains, the significance of this practice grows even more compelling. Organizing collections, adherence to ethical guidelines, and proper maintenance are fundamental to preserving the integrity of these ancient specimens. Furthermore, each fossil can add a story to the vast narrative of Earth’s history.
Ethics of Collecting
Every fossil has a story that deserves respect. Many collectors face moral dilemmas on the line between personal interest and scientific integrity. Ethical collecting encompasses acknowledging the value of fossils not just as objects, but as parts of our natural heritage. Collectors are urged to consider several guidelines:
- Follow Legal Regulations: Familiarity with local laws is paramount. For instance, collecting fossils on public land in Utah might require a permit to ensure sustainability and legal compliance.
- Academic Collaboration: Working with paleontologists can provide insights that elevate the collector's own understanding while contributing to relevant research.
- Respect Cultural Resources: Keep in mind that some fossil sites may contain artifacts of Native American heritage. Recognizing and honoring these cultural significances can prevent conflicts and promote harmony between scientific exploration and cultural appreciation.
Adhering to these guidelines helps cultivate a responsible community of fossil enthusiasts who advocate for the preservation of our planet's history.
Maintenance and Restoration
Once collected, fossil maintenance becomes a priority to ensure they remain safe from damage. Proper care not only extends the life of a specimen but also enhances its educational value. Here are crucial factors to consider in the maintenance of fossils:
- Cleaning: Carefully removing dirt and debris is essential, but avoid aggressive cleaning methods that may damage the fossil’s surface. Soft brushes and gentle techniques often work best.
- Storage: Keep fossils in stable environments to prevent deterioration. Materials such as acid-free boxes or glass cases shield them from dust while providing visibility for showcase.
- Restoration: When dealing with broken or incomplete fossils, restoration can be necessary. However, this should be carried out by professionals or under the guidance of experts to avoid misrepresentation of a specimen.
Proper maintenance is not just about keeping fossils looking good; it’s about preserving the past for future generations.
By following these maintenance strategies and ethical guidelines, collectors can ensure that their contributions to the field of paleontology remain respected, valuable, and sustainable. As more individuals engage with Utah’s fossil heritage, the care taken in collecting and preserving these precious remnants serves as a testament to the respect owed to our planet’s ancient inhabitants.
Community and Public Engagement
Community and public engagement stands as a cornerstone in the field of paleontology, particularly in a state like Utah, where the landscape is rich with dinosaur fossils and history. Engaging local communities not only cultivates a shared appreciation for paleontological heritage but also sparks enthusiasm among individuals of all ages. The benefits are numerous, and understanding them can help bolster support for ongoing and future paleontological initiatives.
Local paleontology groups play a significant role in creating connections between professional researchers and amateur enthusiasts. These groups often organize field trips, workshops, and lectures, which provide valuable opportunities for hands-on learning. Such engagement nurtures a sense of ownership over local history—a sentiment that can lead to increased support for conservation efforts.
In addition, individuals involved in these groups can participate in community excavations, contributing to real scientific research. This collaboration not only enriches the experience of amateurs but also often leads to new discoveries that might otherwise elude professional paleontologists.
"Engagement is not merely about sharing knowledge; it’s about building a community that treasures its paleontological legacy."
Moreover, public engagement serves as a vital feedback loop. Communities that feel involved are more likely to advocate for funding and resources for paleontological research and education. This amplifies voices that might otherwise go unheard in the larger discourse about science and funding allocation.


Local Paleontology Groups
Within Utah, several notable local paleontology groups catalyze this sense of community. Organizations such as the Wasatch Paleo Tribe and the Utah Museum of Natural History Affiliates provide platforms for enthusiasts to gather, share insights, and deepen their understanding of dinosaurs and their environments. These groups frequently host events that draw in families, students, and individuals keen on prehistoric life.
Members of these groups often collaborate on projects like fossil mapping or community digs. Many enthusiasts have reported feeling enriched by these experiences, as they allow individuals to apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings, building skills that can enhance their understanding of geology and paleontology.
These local groups also open the door to networking possibilities. Collaborations with academic institutions help bridge the divide between amateur and professional efforts, often leading to successful publications and shared discoveries.
Educational Outreach
The power of educational outreach cannot be overstated in the context of paleontology. By integrating learning experiences into local schools and community centers, educators spark curiosity and foster a new generation of paleontologists. Across Utah, various programs aim to encourage younger audiences to explore their fossil-rich landscape.
Workshops may include hands-on activities where kids can excavate replica fossils or study real specimens under the guidance of seasoned paleontologists. These initiatives are instrumental in demystifying the world of fossils and igniting a passion for science in youth who might not otherwise have the opportunity to engage with such subjects.
Engaging curriculum that emphasizes local paleontological findings creates relatable contexts for students, making the learning experience more impactful. For teachers, partnering with organizations like the Utah Field House of Natural History provides resources and expertise that enrich classroom experiences dramatically.
In terms of broad community impact, educational outreach has an overflow effect—cultivating a knowledgeable public that appreciates and values the scientific process. This creates a ripple effect in advocacy, funding, and community involvement, ensuring the sustainability of paleontological endeavors for future generations.
By promoting active participation, local paleontology groups and educational initiatives help breakdown barriers, making science accessible and engaging for everyone involved.
Challenges Facing Paleontological Research
Paleontological research, while endlessly fascinating, faces a series of significant hurdles that can complicate our understanding of ancient life. These challenges are not merely academic inconveniences; rather, they can have profound implications on our efforts to uncover the secrets held within the rock layers of Utah and beyond. The focus on these issues is pivotal, especially when considering the diverse paleontological sites all over the state, filled with fossils waiting to tell their stories. Here, we will break down two primary challenges: environmental concerns and funding limitations.
Environmental Concerns
The health of fossil-rich sites is under constant threat from environmental factors. Erosion, climate change, and even human activities like construction and mining can jeopardize these precious paleontological resources. For instance, heavy rainfall can wash away sediment layers that have housed ancient fossils for millions of years, effectively robbing scientists of crucial evidence that could link various species or reveal details about prehistoric environments.
There are ongoing debates about how best to mitigate these impacts. Many paleontologists argue that protecting ecosystems is not just about preserving rocks, but sustaining the context those rocks provide about life long gone. The conundrum lies in balancing extraction activities with conservation efforts. Consider this scenario: A quarry might be rich in fossils, yet the urge to extract materials can lead to irreversible damage. Shoveling tons of earth might yield a few significant finds, but it raises ethical questions about what we are willing to sacrifice to learn more about our planet’s history.
"Protecting these fossil sites is crucial not just for science, but for cultural heritage. Once these fossils are lost, we may never understand how they shaped the ecosystems we see today."
Funding Limitations
Funding has been a thorny issue in paleontology, particularly in Utah, a state rich with discoveries but often lacking adequate financial support for research initiatives. Grants for fieldwork, excavation tools, and museum exhibitions are only a few things that demand funding; yet it remains scarce. Consequently, many researchers find themselves undertaking projects on shoestring budgets, often out of their own pockets.
Such limitations can delay research and discourage fresh talent from entering the field. Aspiring paleontologists may find themselves in a struggle, as cutting-edge research requires more than just passion—it needs sufficient backing. Some notable consequences include:
- Project delays: Many significant studies can stall due to lack of initial funding, pushing discoveries further into the future.
- Reduced outreach: Limited funds often mean fewer educational programs to engage the public, contributing to a less informed community that might not appreciate these vital resources.
- Talent drain: Younger scientists may opt for more stable fields, leaving behind a shortage of manpower essential for continued research.
Future Directions in Dinosaur Paleontology
As we venture into the future, the conversation around dinosaur paleontology in Utah and beyond is bafflingly exciting. New discoveries and innovations are occurring at breakneck speed, reshaping our understanding of how these magnificent creatures lived, thrived, and ultimately perished. The importance of this topic cannot be overstated; the answers we uncover continue to lay the groundwork for future research and provide insight into ancient ecosystems.
Technological Advances
Computer Simulations
Computer simulations have emerged as a game changer in paleontology, allowing researchers to recreate ancient environments and model dinosaur behavior with impressive accuracy. This technology takes advantage of vast data sets from fossil records, geological formations, and modern animal behaviors. With simulations, scientists can test hypotheses about how dinosaurs might have interacted with their surroundings.
One key characteristic of computer simulations is their ability to predict various scenarios that fossil evidence alone cannot clarify, shedding light on how climate and geography might have influenced dinosaur life. In this paper, we recognize the importance of this technology – it’s a popular choice for researchers looking to bridge gaps in knowledge.
However, there are certain unique features that come with this method. For one, it allows rapid testing of multiple variables without the logistical hurdles of fieldwork. Yet, the downside includes the fact that these models sometimes rely too heavily on assumptions, which can lead to skewed interpretations if not managed correctly.
Genetic Research
Turning our gaze to genetic research reveals even more fodder for curiosity. Advances in this field are enabling scientists to extract genetic material from fossils, even those millions of years old. This aspect doesn’t just focus on dinosaurs, but it also paves the way for broader evolutionary studies that track changes over time.
The key characteristic of genetic research lies in its ability to connect extinct organisms to their living relatives. This offers a beneficial angle for further studies, adding a level of depth to our understanding of evolutionary pathways. The unique feature of this research is the use of sophisticated techniques like CRISPR and other genetic editing methods, which can contribute to de-extinction discussions and help us understand adaptation mechanisms.
However, the struggle comes from public misconceptions and ethical dilemmas regarding manipulation of ancient genes, stirring debates that could influence research funding and policies.
The Next Frontier of Discoveries
The horizon is ripe with potential discoveries that could reshape how we see dinosaurs in Utah. With every new fossil uncovere, there are mysteries waiting to be solved. One promising area involves remote location excavation where sites remain untapped. In addition, collaborations between paleontologists, universities, and tech companies are blossoming, combining traditional science with cutting-edge technology to reveal more than we could ever imagine.
Researchers are now starting to explore previously undisturbed layers of rock, where fresh fossils could yield radical insights. As we embrace these new frontiers, we acknowledge that the journey through paleontology is not just about the bones themselves but about building a narrative of life on Earth.
"Each fossil holds stories from the past, and every new technology helps us decode these ancient narratives."
In sum, the future is bright for dinosaur paleontology, bringing with it the promise of innovative techniques and collaborative efforts that will deepen our understanding of these remarkable creatures and their world. The active involvement of collectors, enthusiasts, and researchers can only enhance this exploration, helping to keep the flame of curiosity alive.
Epilogue
In wrapping up our exploration of dinosaur fossils in Utah, it becomes evident that this topic holds a treasure trove of significance both for enthusiasts and researchers alike. Understanding the depth of Utah's paleontological landscape sheds light on how the Mesozoic Era unfolded, and why these remnants of the past continue to shape our understanding of life on Earth.
Summary of Key Insights
Throughout this article, we've traversed the intriguing world of Utah's dinosaur fossils, highlighting several key insights:
- Geological Richness: Utah’s unique geological formations, such as the Morrison and Cretaceous Mudstone, provide a rare window into the landscapes that dinosaurs once roamed.
- Diverse Discoveries: The state alone has yielded famous finds like the Allosaurus, Stegosaurus, and Utahraptor, revealing a variety of species that thrived in different epochs.
- Methodologies of Excavation: In learning about excavation and preservation techniques, we appreciate the meticulous craft that goes into ensuring these fossils are safeguarded for future generations.
- Community Engagement: The local paleontology groups and educational outreach programs foster a culture of curiosity and conservation, ensuring that the next generation values these ancient wonders.
- Future Endeavors: With the advent of technology in paleontological research, we are on the brink of new discoveries that may reshape our understanding of these ancient creatures.
Encouraging Continued Exploration
As we conclude, it’s essential to emphasize the need for continued exploration and study of Utah's dinosaur fossils. The field of paleontology is ever-evolving; each new fossil discovery can change the narrative we understand about prehistoric life. For rock and fossil collectors, there is a call to participate actively in this endeavor—whether through documentation, ethical collecting practices, or supporting local museums and institutions.
Such involvement not only enriches personal understanding but contributes to a wider appreciation of our Earth’s geological history. There remains so much to uncover, from unearthing potential new species to understanding the ecological networks of the past. This timeless quest—driven by both curiosity and method—holds the promise of paving the way for future generations to further chase the mysteries hidden beneath our feet.
The wonders of the past are directly woven into the fabric of the present; by exploring them, we not only honor those who came before us but deepen the narrative of our shared existence.
If you’re interested in delving deeper into these topics, consider engaging with local paleontology societies, visiting dinosaur fossil sites, or even participating in excavation activities. After all, every rock tells a story waiting to be uncovered.



