Exploring the Fascinating World of Meteorite Stones


Intro
Meteorite stones capture the fascination of both scientists and collectors. They provide a glimpse into the cosmos, offering insights into events that shaped our solar system. This article intends to systematically explore the various aspects of meteorite stones. From their origins amidst the asteroids and comets to their classifications and significance in scientific research, each facet of meteorites reveals a rich tapestry of knowledge.
In addition, the discourse on identification, authentication methods, and responsible collecting practices will enhance the appreciation of these unique specimens. Moreover, by understanding the care and preservation of meteorites, collectors can protect their investments and maintain the integrity of their collections. This comprehensive examination serves not only to inform but also to deepen the engagement of enthusiasts in the world of meteorites.
Preface to Meteorite Stones
Meteorite stones hold a special place in the sciences and among collector communities. Their study is not just a pursuit of curiosity but also a gateway to understanding the formation and make-up of our solar system. This article aims to elucidate various facets of meteorites, emphasizing their significance in both scientific and cultural contexts. By aggregating knowledge on meteorite classification, authenticity, collection practices, and preservation, we can illuminate the remarkable journey of these celestial objects from outer space to earthly hands.
Definition and Importance
Meteorites are fragments of rock or metal that originate from outer space, specifically from asteroids or other celestial bodies, and fall to Earth. Their importance lies in the unique information they provide about the early solar system and the processes that shaped the planets. Studying meteorites contributes significantly to mineralogy and geology, offering insights unavailable from terrestrial samples. Additionally, these stones help us understand planetary formation and evolution, which is crucial in the field of space exploration.
Some meteorites carry isotopes that reveal the age of the solar system, while others contain organic compounds that may hint at the origins of life. The presence of various minerals in meteorites offers a broader perspective on planetary materials, aiding in the development of our understanding of Earth's geology.
Cultural Significance of Meteorites
Beyond their scientific value, meteorites possess a rich cultural significance that spans centuries. Many ancient civilizations revered meteorites as divine or mystical objects, often incorporating them into religious practices or artifacts. The belief in their otherworldly origin piqued interest, drawing attention from scholars and collectors alike.
In modern times, meteorites continue to capture the public's imagination. They are featured prominently in popular culture, literature, and art. Collectors chase meteorites not just for their value but for the stories they tell about our universe. The intersection of science and culture makes meteorites unique, serving as a reminder of humanity's connection to the cosmos and our perpetual quest for knowledge.
"Meteorites are time capsules that connect us to the beginning of our solar system."
Understanding both their scientific and cultural backgrounds enhances the appreciation of these stones. As meteorite enthusiasts delve into collections, they do not just accumulate items but historical artifacts that hold the narrative of the universe itself.
The Science Behind Meteorites
The study of meteorites holds great significance in understanding not just the stones themselves, but also the broader context of our solar system. Meteorites provide a unique link to the early solar system, giving researchers insight into the conditions that existed during its formation. By examining the composition, structure, and isotopic signatures of these celestial objects, scientists can better understand planetary formation processes and the evolution of various celestial bodies. This examination is beneficial because it allows for a more comprehensive grasp of planetary sciences and the origin of elements found on Earth.
Formation and Composition
Meteorites are remnants of material that formed in the early solar system. Most meteorites originate from asteroids, which are leftover building blocks from the formation of planets. When asteroids collide, fragments break off, and these fragments can enter Earth's atmosphere. Upon landing, they are referred to as meteorites.
Meteorites can be classified primarily based on their mineral composition. They often contain silicate minerals, metals, and other elemental compounds. The study of their specific composition can reveal clues to their origin and the conditions under which they formed. Understanding their formation is critical for piecing together the timeline of our solar system's development.
Types of Meteorites
Meteorites can be divided into several types, each offering its unique insights into cosmic processes.
Stony Meteorites
Stony meteorites make up the majority of meteorite finds. They primarily consist of silicate minerals, with a composition similar to that of the Earth's crust. The significance of stony meteorites lies in their ability to offer clues about the early state of the solar system. Their common mineral constituents include olivine and pyroxene, which are also found in terrestrial rocks. This connection can help researchers draw parallels between extraterrestrial and Earthly processes. Key characteristics of stony meteorites include their often fragmented appearance and relative lightness compared to their iron counterparts. This makes them a popular choice among collectors because they are often visually striking and more accessible than rarer types. However, they can also be more challenging to identify compared to iron meteorites.
Iron Meteorites
Iron meteorites are primarily composed of nickel and iron, often exhibiting a striking metallic appearance. Their origin is typically linked to the cores of differentiated asteroids. Studying iron meteorites is essential because their structures can provide direct insights into the processes that occurred during the formation of planetary bodies. One of the key characteristics of iron meteorites is their high density compared to stony types, which makes them easier to identify. Their metallic nature often leads to greater interest from collectors, making them a valuable addition to any collection. However, their rarity compared to stony meteorites means they can be much more expensive.
Stony-Iron Meteorites
Stony-iron meteorites are a hybrid class that contains both metallic and silicate minerals. This combination leads to unique features that can provide critical information about the conditions existing within the parent bodies. These meteorites often represent the boundary between the metal-rich cores and the silicate mantles of differentiated asteroids. They are somewhat less common than the other types but are very desirable due to their mixed composition. Stony-iron meteorites can display a fascinating array of textures and colors, making them visually intriguing. However, their novelty and complexity can sometimes complicate their identification and classification, presenting both challenges and opportunities in scientific inquiry.
By studying meteorites, scientists can gain critical insights into the history of our solar system and the processes that shaped its development.
Understanding the various types of meteorites is vital for both collectors and researchers. Each classification provides differing perspectives on the history of celestial objects, enriching the overall knowledge of astronomical phenomena.
Historical Context of Meteorite Discoveries
Understanding the historical context of meteorite discoveries provides essential insights into how these celestial rocks have captivated humans for centuries. This context is crucial as it shows the evolution of human interaction with meteorites, from ancient beliefs to modern scientific study. The study of meteorites is not only about their geological characteristics but also about human perception and reaction to these extraterrestrial visitors.
Earliest Recorded Finds
The earliest recorded finds of meteorites date back to ancient civilizations. One of the most significant examples is a meteorite that fell in the vicinity of the city of Siena, Italy, around 2000 BC. These early encounters shaped how meteorites were interpreted, often regarded as divine messages or omens. Another impressive example is the Tunguska event in 1908, where a massive explosion in Siberia is believed to have resulted from an airburst of a meteoroid. Both instances highlight early human curiosity mixed with mythology and fear.
From cultures that worshiped meteorites as sacred stones to those who viewed them with suspicion, early responses influenced subsequent studies. The ancient Greeks even classified meteorites, using terms like "meteoron." Collectively, these findings contributed to the foundational understanding and appreciation of meteorites, serving as a stepping stone for future research.
Significant Meteorite Events
Several remarkable meteorite events have left profound impacts on both scientific fields and public imagination. Notable meteor storm events, such as the Leonid meteor shower in late 1832, brought a wave of interest to astronomy and the study of meteorites. Researchers began documenting these occurrences, marking a shift toward a more systematic approach to meteorological phenomena.
Additionally, the discovery of the Allende meteorite in 1969 in Mexico is a key milestone. As one of the largest meteorites ever found, it opened a new chapter in scientific research and provided invaluable data about the solar system's formation. The insights gained from Allende significantly enhanced our understanding of cosmic materials and their properties.
"Meteorites are not just relics from space; they provide clues about our cosmic origins and the evolution of the solar system."
In the 20th century, with advancements in technology and proper classification systems, meteorite research flourished. These historical contexts underscore the fact that meteorites embody both scientific and cultural importance, shaping human perspectives and endeavors throughout time. In essence, these meteorite events demonstrate the intertwined nature of science, history, and human emotion in our quest to understand the universe.
Identifying Meteorite Stones


Identifying meteorite stones is critical for enthusiasts and collectors. Misidentification can lead to lost opportunities and potential monetary loss. The characteristics that distinguish meteorites from terrestrial rocks include their unique composition and physical attributes. An understanding of these identifiers can enhance credibility when collecting and trading meteorites, which drives value in the market.
Key Characteristics
Meteorites possess distinct features that set them apart from regular rocks. Some of the primary characteristics include:
- Fusion crust: This is a thin, glassy exterior formed when the meteorite burns up during its entry into the Earth's atmosphere.
- Density: Meteorites are typically denser than average rocks. They might feel heavier when compared to similar-sized terrestrial stones.
- Magnetism: Many meteorites are metallic and exhibit magnetic properties, which can help during identification.
- Chondrules: These are small, round particles found in some stony meteorites, lending insight into their formation processes in the early solar system.
Familiarizing oneself with these defining features aids in separating genuine meteorites from imitations. Collectors can learn to note these characteristics through experience and research.
Testing Methods
Accurate identification requires testing methods. Each method carries its own advantages and limitations, serving collectors in various contexts.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection involves a careful examination of a meteorite's physical properties. Collectors often look for features such as fusion crust and chondrules. This method is quick and does not require specialized equipment, making it a common first step in identification. However, it relies heavily on the experience of the individual conducting the inspection.
One drawback exists: common terrestrial rocks can sometimes mimic the appearance of meteorites.
Chemical Analysis
Chemical analysis provides a deeper insight into the composition of a meteorite. This method uses techniques like X-ray fluorescence to determine elemental make-up. It confirms whether the mineral content characterizes known meteorite types, offering a precise identification method.
Though chemical analysis is accurate, it requires access to sophisticated laboratory equipment and expertise, which can be barriers for many hobbyists.
Magnetic Testing
Magnetic testing assesses the magnetic properties of a suspected meteorite. The presence of nickel and iron indicates a probable meteorite, as these metals are prevalent in many known types. This method is relatively simple and can provide quick results, informing collectors if further testing is needed.
However, not all meteorites are magnetic. Some may lack these magnetic characteristics, leading to potential misidentification.
Understanding the nuances behind identifying meteorite stones is essential for collectors. The knowledge gained through visual inspection, chemical analysis, and magnetic testing can ensure authenticity and value in a collector’s portfolio.
Meteorite Authentication Process
The process of authenticating meteorites is crucial, particularly for collectors and researchers alike. Authenticity verifies that a stone is indeed a meteorite and not a terrestrial rock masquerading as one. This verification not only affects the value of the specimen but also informs the scientific significance of the material. A genuine meteorite can provide insights into the formation of the solar system, planetary processes, and even the history of Earth itself.
Importance of Authenticity
Authenticity is significant across multiple dimensions. First, many collectors invest substantial sums into acquiring meteorites. A lack of authenticity may lead to financial losses and severely damage a collector’s reputation within the community. Moreover, authenticated meteorites often hold greater scientific value, helping researchers understand various planetary phenomena.
It is essential to highlight that many meteorites in circulation are misidentified. The similarity in appearance between some meteorites and common terrestrial rocks can mislead buyers. Thus, understanding their authenticity can safeguard collectors and enthusiasts from potential deceptions.
A key point to consider is that meteorite authentication goes beyond some basic tests. It can involve complex scientific analyses, ensuring that any specimen is rigorously examined before declaring it authentic.
"An authentic meteorite not only confirms its cosmic origin but also adds distinctive value to collections, contributing knowledge to both science and collectors' heritage."
Consulting Experts
When in doubt, consulting experts is an effective step in the authentication process. Many museums and academic institutions have specialists focusing on meteoritics. They utilize advanced techniques for analyzing meteorite samples, including isotopic studies and X-ray diffraction. Such analyses can reveal vital details about the composition and structure of the meteorite, which helps confirm its authenticity.
Moreover, reputable dealers often maintain connections with scientific institutions. They can provide contacts or even submit samples for analysis, ensuring that buyers receive what they pay for. This reliance on expert opinions fosters trust within the community and promotes ethical practices in meteorite trading.
Collecting Meteorites
Collecting meteorites is a fascinating and complex endeavor that merges the worlds of science and hobby. The appeal lies not only in their otherworldly origins but also in the stories they carry from the vastness of space. For enthusiasts and collectors, these stones symbolize a direct connection to celestial events that have shaped our planet and the solar system as a whole.
The importance of collecting meteorites extends beyond mere acquisition. It can lead to a better understanding of planetary formation and evolution. Each meteorite offers unique insights into the history of our solar system, allowing collectors to contribute to the academic discourse within planetary science.
From an aesthetic standpoint, meteorites are remarkable objects, often carrying distinctive features and colors that highlight their extraterrestrial origins. Collectors may focus on owning various types of meteorites, such as stony, iron, or stony-iron types, each bringing its own unique story and characteristics.
Collector's Guide
Starting a collection of meteorites can be both rewarding and challenging. A collector's guide can help navigate the initial steps and equip individuals with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
- Research: Knowledge is the key to successful collecting. Study different types of meteorites, their classifications, and their relevance in scientific discussions. Check reputable sources online, including Wikipedia and Britannica.
- Purchasing: When looking to buy, ensure to purchase from reputable dealers or auctions. Trustworthy sources will provide certificates of authenticity, which are crucial for establishing provenance.
- Display: Proper display is essential to preserve the integrity of your collection. Utilize protective cases and keep your meteorites away from direct sunlight and severe temperature fluctuations.
- Documentation: Keep thorough records of each piece, including its classification, origin, purchase date, and relevant characteristics. This documentation not only enhances the value of the collection but also offers rich historical context.
Ethical Considerations
As meteorite collecting grows in popularity, ethical considerations have become increasingly crucial. Collectors must navigate the fine line between personal interest and responsible collecting practices.
- Legal Regulations: Understand the legal frameworks surrounding meteorite collection. Different countries have varying laws regarding ownership, and some regions may restrict the collection of meteorites from protected lands. Always ensure compliance with local and international regulations.
- Respect for Scientific Research: Many meteorites are essential for ongoing scientific studies. Collectors should consider donating specimens to research institutions to support education and academic pursuits.
- Conservation of Natural Resources: The collection should not threaten meteorite populations or their surrounding environments. Practicing responsible collecting habits ensures future generations can also appreciate these celestial treasures.
In summary, collecting meteorites is a pursuit that blends personal enjoyment with respect for scientific inquiry and ethical integrity. Enthusiasts can navigate this complex landscape by arming themselves with knowledge and adopting responsible practices.
Care and Preservation of Meteorites
Caring for and preserving meteorites is essential for maintaining their scientific and aesthetic value. Meteorites are not just rocks; they are remnants of the solar system's formation and hold vital clues to its history. Proper care ensures that these invaluable specimens endure through time, retaining their integrity and significance for future study and appreciation. A well-preserved meteorite can provide insights into planetary formation, the geological processes of other bodies, and even the conditions of the early solar system. Moreover, collectors should be aware of how environmental factors can impact these stones, making preservation a key responsibility.
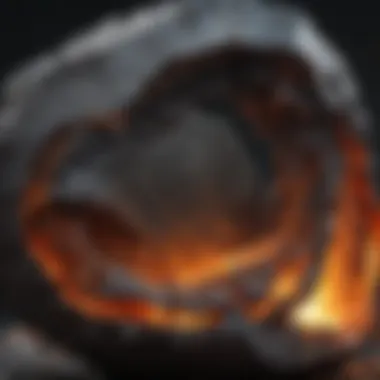
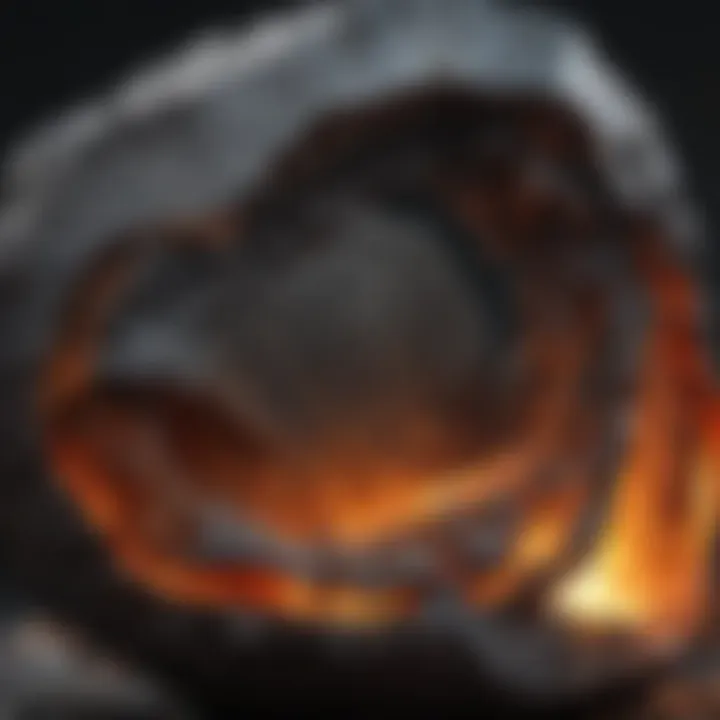
Storage Recommendations
Storing meteorites correctly is crucial to prevent damage. Excess moisture, temperature fluctuations, and physical impacts can lead to deterioration.
Here are some recommendations for optimal storage:
- Use airtight containers: Preserve meteorites in sealed boxes or plastic bags with desiccants to absorb moisture.
- Control environment: Keep the storage area dry and stable. Fluctuating temperatures can lead to oxidation, especially in metal-rich types.
- Avoid direct sunlight: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can fade the surface and alter the mineral structure.
- Label correctly: Always label your meteorites accurately, including their classification and discovery details, for future reference.
Following these steps helps to keep the specimens intact and research-ready.
Cleaning Techniques
When cleaning meteorites, it is important to maintain their natural state while removing any contaminants. Improper cleaning can lead to irreversible damage, hence caution is paramount.
Consider these techniques:
- Avoid harsh chemicals: Stick to distilled water and a soft brush for basic cleaning. Abrasive tools can scratch or alter the surface.
- Gentle brushing: Use a soft-bristled brush to carefully remove dirt. Take care not to apply too much pressure.
- Dry thoroughly: After cleaning, ensure to dry the meteorite completely before storage to prevent moisture-related issues.
By adopting these practices, collectors and enthusiasts can effectively manage their meteorites, ensuring that these fascinating stones retain their value and contribute to ongoing research.
Meteorites in Popular Culture
Meteorites hold a gripping role in popular culture, capturing the imagination of society and influencing a variety of creative expressions. Their enigmatic nature and extraterrestrial origins not only fascinate scientists and collectors but also inspire authors, artists, and filmmakers. This connection underscores the societal relevance of meteorite stones, showcasing their impact and importance.
Meteorites in Literature and Art
Literature has often explored the theme of meteorites, weaving them into tales that analyze humanity's place in the universe. Authors have used meteorites as symbols of change, discovery, or unexplained phenomena. For example, H.G. Wells’ The War of the Worlds features a meteor crash that leads to the arrival of extraterrestrial beings, reflecting humans' fears and curiosity about life beyond Earth.
In visual art, meteorites have appeared as motifs in various forms, from paintings to sculptures. Artists use meteorites to express themes of chaos, beauty, and the unknown. The physical presence of these stones speaks to the transience of life and the cosmic origins of existence. Notably, contemporary installations often utilize actual meteorite fragments, further blurring the lines between art and science.
Influence on Science Fiction
Science fiction has prominently featured meteorites, depicting them as harbingers of awe-inspiring or catastrophic events. They often serve as vehicles of alien life or advanced technology. Works such as Arthur C. Clarke’s The Sentinel, which later inspired the film 2001: A Space Odyssey, present meteorites as gateways to greater understanding of the cosmos. Such narratives tap into humanity's yearning for exploration and the potential knowledge hidden in the universe.
The fascination with meteorites extends beyond entertainment into deeper societal reflections. They challenge perceptions about human existence and our responsibility toward planetary stewardship. Furthermore, by presenting meteorites as both danger and discovery, popular culture reinforces the idea that these celestial stones carry significant weight in our comprehension of science and imagination.
"Meteorites serve as a bridge between our earthly existence and the mysteries beyond. They remind us of our shared universe and the stories waiting to be told."
In sum, the portrayal of meteorites in popular culture not only enriches creative expressions but also provokes thought about broader cosmic implications. It reflects society's ongoing intrigue with the unknown and our position in the vast tapestry of the universe, making meteorites not just a subject of collection but a symbol of exploration.
Meteorites and Scientific Research
Understanding meteorites is essential for both scientific inquiry and the growth of knowledge about our solar system. Scientists examine meteorites not just as space rocks but as valuable entities that provide insight into the conditions of the early solar system. Their study reveals the composition of asteroids and the processes that led to planet formation. Moreover, meteorites can contribute to various scientific fields, including geology, astronomy, and even biological sciences.
Contributions to Understanding the Solar System
Meteorites serve as remnants of celestial bodies formed during the early solar system. By analyzing the materials within meteorites, researchers gain access to information about the chemical makeup and thermal history of other planetary bodies. This makes them crucial in piecing together the narrative of how planets like Earth came into existence.
Some specific elements of importance include:
- Isotopic Analysis: Meteorites allow scientists to measure isotopes, which can reveal the age of these materials. This helps construct timelines for cosmic events.
- Mineralogical Composition: The minerals found in meteorites provide clues to the environments they originated from. For instance, specific minerals indicate either high or low temperature conditions, aiding in understanding planetary differentiation.
"Meteorites are time capsules. They tell us about the solar system's past, revealing the secrets that are impossible for us to gather through Earth-bound observations."
The implications of meteorite research extend beyond just academic interests. They offer insights that could influence future space missions, enabling scientists to select target locations based on material composition analysis.
Meteorites in Planetary Science
In planetary science, meteorites are invaluable for establishing relationships between terrestrial planets, asteroids, and comets. Many meteorites are classified into categories based on their origin, like achondrites or chondrites, which helps scientists identify the parent bodies from which they come.
Here are a few points that signify the relevance of meteorites in this field:
- Comparative Planetology: By studying meteorites that originate from different celestial bodies, researchers can compare and contrast these materials with terrestrial samples. This comparison showcases the similarities and differences in material composition.
- Impact Events: The geological history of Earth is closely tied to impact events. Meteorites can provide data about these impacts, including size and frequency, contributing to our understanding of Earth's evolution.
- Potential for Life: Research into meteorites has unveiled organic compounds and amino acids. These discoveries raise stimulating questions about the existence of life beyond Earth.
Ultimately, meteorites are like dynamic archives of the cosmic history that surround our planet. Their analysis not only enhances our scientific comprehension but also provides a solid foundation for future exploratory missions and research initiatives.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Meteorite Collection
The collection of meteorites involves several legal and ethical considerations that are crucial for both collectors and the scientific community. Understanding these implications ensures that collectors act responsibly while also preserving the scientific integrity of meteorite specimens. The interest in meteorite collecting has surged, bringing attention to the regulatory aspects that govern this practice.
Regulatory Framework
Meteorites are often considered natural artifacts, and their ownership can fall under various laws depending on the country or region. Many nations have specific regulations concerning the collection and sale of meteorites. For example, in the United States, the U.S. Government generally allows private ownership of meteorites found on private land. However, the situation changes when meteorites are found on federal land, where they are considered property of the government.
Internationally, different countries impose restrictions on the exportation of meteorites. Countries such as Mexico and parts of Africa have strong regulations, reflecting the belief that meteorites are part of national heritage. Collectors must be aware of these regulations to avoid legal issues that can arise from unauthorized collection or sale. Additionally, organizations like the International Meteorite Collectors Association help clarify ethical standards and practices.
Responsible Practices for Collectors
Adopting responsible practices when collecting meteorites is essential for preserving both individual rights and the greater scientific value of these stones. Here are several guidelines that collectors should follow:

- Know the Law: Familiarize yourself with local, national, and international laws governing meteorite collection. This ensures you remain compliant and avoid potential penalties.
- Respect Land Rights: Always obtain permission from landowners before collecting on private property. Collecting without consent can lead to disputes and legal challenges.
- Document Finds: Maintain accurate records of any meteorites collected, including where and when they were found. This information can be crucial when establishing provenance.
- Skip the Scams: Be vigilant against unethical sellers who may misrepresent meteorites' origins or authenticity. Educating oneself on common fraud tactics can help avoid this pitfall.
- Contribute to Science: Consider donating or loaning specimens to museums or educational institutions. This can enhance public knowledge and appreciation of meteorites while ensuring that valuable samples are preserved for research.
"Understanding the legal landscape of meteorite collection is as critical as the passion for collecting itself. Engage ethically to preserve the scientific value and cultural significance of meteorites."
Following these practices will not only protect collectors but also ensure that meteorite studies continue to thrive without disrupting the potential for future discoveries. Ultimately, a conscientious approach fosters a community that respects both the treasures of space and the rules that govern their collection.
Meteorite Auctions and Market Trends
In the realm of meteorite collecting, auctions play a crucial role. They provide a platform where collectors, enthusiasts, and investors can acquire unique specimens and rare finds that might not be available through conventional channels. The dynamics of meteorite auctions reveal much about the current market trends, collector interests, and the overall valuation of these extraterrestrial rocks.
Understanding the Meteorite Market
The global market for meteorites has seen considerable growth in recent years, attracting both serious collectors and casual enthusiasts. Various factors contribute to this burgeoning interest.
- Rarity and Value: Many meteorites are rare, and their value often appreciates over time. This makes them an attractive investment for collectors who understand the significance of specific finds.
- Scientific Interest: As our understanding of space and planetary science evolves, so does interest in meteorites. They offer insight into the early solar system, contributing to research and education.
- Cultural Fascination: The mystery surrounding meteorites—originating from space—captivates the imagination. This cultural allure often drives demand in the market.
Websites such as Wikipedia provide additional background information on meteorite classification and significance. Understanding these aspects can greatly enhance collectors' appreciation and knowledge.
Notable Auction Sales
Auction events have showcased some remarkable meteorite sales over the years, highlighting both the beauty and scientific value of these cosmic specimens. Here are a few standout examples that are often referenced within the collector community:
- The Allende Meteorite: Auctioned for a significant sum, this piece is famous for being the largest carbonaceous chondrite ever found. Its sale illustrated the market's potential for high-value meteorites.
- The Neuschwanstein Meteorite: This iron meteorite has garnered attention for both its aesthetic and scientific properties. Its auction highlighted the balance collectors seek between beauty and scientific interest.
- The Basankusu Meteorite: An auction of this specimen showcased the increasing interest in meteorites from lesser-known falls, emphasizing a trend toward diversification in collecting.
These auctions are not just transactional; they reflect changing interests and innovations in collecting practices. By tracking notable sales, collectors can gauge market trends and make informed decisions regarding their own purchases.
"The value of meteorites is not just in their material worth but in the stories they tell about our universe."
In summary, meteorite auctions serve as both a marketplace and a barometer for the collector community. Understanding the underlying factors in the meteorite market and keeping an eye on notable sales can empower both new and experienced collectors to navigate this fascinating field.
Educational Resources for Meteorite Enthusiasts
Understanding meteorites requires not only curiosity but also access to quality information. Educational resources play a crucial role for meteorite enthusiasts. They offer insights into the complexities of meteorite classification, collection practices, and the science behind these celestial stones. Enthusiasts often seek trustworthy materials to deepen their knowledge and enhance their collection efforts.
The availability of quality books, journals, and online platforms can significantly impact one’s understanding of meteorites. These resources provide historical context, technical details, and updates on ongoing research. Furthermore, they facilitate community engagement which is essential for learning and sharing experiences. Without such resources, it can be challenging to grasp the fascinating and intricate world of meteorites.
Books and Journals
Books and journals are fundamental tools for any meteorite enthusiast aspiring to understand this field thoroughly. Titles like The Meteorite Catalog and The Cosmogenic Isotope Method can provide in-depth knowledge, including the identification, origins, and types of meteorites.
Journals such as Meteoritics & Planetary Science publish peer-reviewed articles that are invaluable for anyone serious about research in this domain. These publications often highlight the latest studies and discoveries, making them a vital reference for both academics and collectors.
Consider investing in a library of books focused on meteorite classification, meteorite hunting tips, and stories from collectors. It is worthwhile to note the differences in perspectives offered by various publications. They can vary from academic to more practical, collector-focused readings.
Online Communities and Forums
Online communities are thriving spaces where enthusiasts from around the world converge to share insights and challenges. Platforms like Reddit and Facebook host groups specifically dedicated to meteorite discussions. These platforms allow users to post questions, share findings, and discuss authenticity, all while learning from collective experiences.
Engaging in forums can provide real-time updates about meteorite events, auction alerts, and legal matters impacting collectors. It brings together beginners and experienced collectors, creating an environment rich with knowledge and practical advice.
Being an active member in these online spaces not only enhances your understanding of meteorites but also builds connections with like-minded individuals. This sense of community can lead to invaluable advice and even potential trading opportunities among collectors.
Online resources and communities empower meteorite enthusiasts by providing real-time updates and fostering connections.
Future of Meteorite Research
Meteorite research is entering a new era, driven by advancements in technology and a growing understanding of planetary formation. Understanding the future of meteorite research is important for several reasons. First, it opens up greater possibilities for scientific discoveries that can reshape our understanding of the solar system. Second, it offers collectors a chance to gain insights into the value and significance of their collections. Third, the integrations of new methodologies can lead to improved authentication processes, ensuring that collectors know they are acquiring genuine specimens.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are a cornerstone of modern meteorite research. Techniques such as high-resolution imaging and molecular analysis provide researchers with tools to explore meteorites at unprecedented levels of detail. For instance, tools like scanning electron microscopes allow scientists to examine microstructures in meteorites, shedding light on their formation processes.
Additionally, advancements in isotopic analysis help to trace the origins of meteorites, linking them back to specific asteroids or planetary bodies. This can deepen our understanding of celestial events that shaped our solar system millions or billions of years ago. Data analytics is also evolving rapidly, enabling researchers to analyze vast amounts of information from meteorite samples. These technologies pave the way for more precise studies and encourage innovative research designs that can explore previously uncharted territories in planetary science.
Potential Discoveries
The potential discoveries in meteorite research are vast and exciting. As techniques improve, researchers may uncover new types of meteorites that have not been classified yet. These findings could provide insights into the early solar system, especially regarding the processes that led to the formation of planets. Unique materials or minerals found in these meteorites might also present new opportunities for industrial applications.
Moreover, studying meteorites from specific asteroids could supply information about raw materials that may be utilized in future space exploration missions. As missions to these celestial bodies become realistic, the findings from meteorite samples could directly influence strategies for resource utilization in space. To summarize, the future of meteorite research holds promise for scientific advancement, deeper insights into our solar system, and increased engagement in the collector community.
New methods and technologies constantly reshape our understanding of meteorites, promising to unveil secrets from the universe's past.
End
The conclusion of this article serves as a pivotal component, summarizing the intricate themes surrounding meteorite stones. It underscores their significance not only in scientific study but also within collecting communities. As we wrap up our exploration, it is essential to recognize the wealth of knowledge that meteorites provide about the cosmos. These earthly fragments, born from the vastness of space, connect the past, present, and future of our universe.
Summary of Key Points
This article highlighted several vital aspects of meteorite stones:
- The origin and formation of meteorites, linking them to events in the early solar system.
- The classification of meteorites, including stony, iron, and stony-iron types.
- The cultural and historical relevance of meteorites, including significant discoveries and how they have influenced various fields.
- Methods for identifying and authenticating meteorite specimens, which are crucial for collectors and researchers alike.
- The ethical considerations surrounding meteorite collection, emphasizing the responsibility of collectors to adhere to guidelines and best practices.
- Educational resources and future directions in meteorite research that promise to further expand our understanding of these fascinating stones.
Final Thoughts on Meteorite Stones
Reflecting on our discussions, meteorite stones captivate not only for their scientific implications but also for their aesthetic and cultural allure. They symbolize a bridge between our planet and the vastness of space, igniting curiosity in many. Collectors and enthusiasts play an essential role in preserving this connection and fostering appreciation for the natural world. As research continues, the potential for new discoveries remains high, making the study of meteorites not only rewarding but essential in decoding the mysteries of our universe. Let each meteorite serve as a reminder of our quest for knowledge and understanding, a tangible piece of the cosmos right in our hands.



