Cracking a Geode: An In-Depth Guide
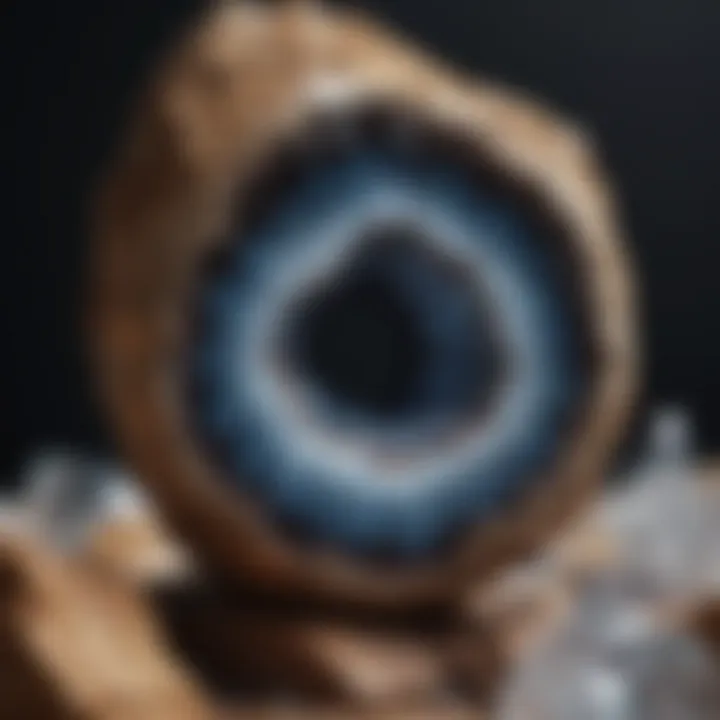

Intro
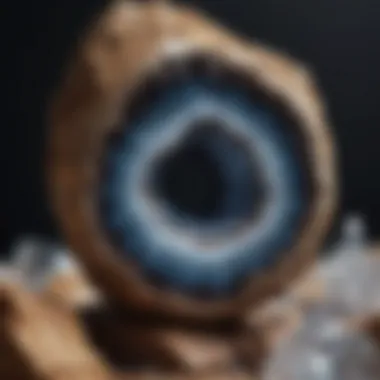
Geodes captivate the imagination with their hidden beauty and intricate formations. These natural wonders, often posing as ordinary rocks, can reveal stunning crystals and mineral deposits once cracked open. Understanding the process of cracking geodes requires knowledge of geology, safety measures, and the right techniques. This article will serve as a comprehensive guide for rock and fossil collectors, hobbyists, and anyone intrigued by the mysteries of the Earth.
The allure of geodes stems not only from their physical characteristics but also from their formation process. Essentially, geodes are the result of mineral-rich water filling cavities in rocks, where minerals crystallize over time. Factors like temperature, pressure, and the chemical composition of water influence the types of minerals present inside.
To successfully crack a geode, one must be equipped with appropriate tools and safety precautions. The following sections will outline the essential aspects of this process, including featured collectibles, identification techniques, and tips for preservation. The objective is to encourage a deeper appreciation for these geological formations and to provide valuable insights for extracting their beauty.
Featured Collectible of the Month
Overview
This month, we shine a spotlight on the stunning amethyst geode. Known for its striking purple crystals, the amethyst geode stands out among its peers. Found mainly in Brazil and Uruguay, these geodes can display an array of colors, but the purple hue is significantly sought after by collectors.
Historical Significance
Amethyst has a rich historical backdrop, once believed to possess protective properties. Ancient Greeks wore amethyst jewelry to prevent intoxication, believing it contained mystical powers. Today, it remains popular not only for its aesthetic appeal but also for its metaphysical attributes. Collectors and enthusiasts highly value amethyst geodes for both their beauty and historical connections.
Identification Techniques
Identifying geodes can be crucial for determining their potential value and beauty. Here are some practical methods for recognizing geodes and distinguishing them from regular rocks.
Visual Characteristics
- Shape: Geodes are typically spherical or oval in shape, but can be irregular.
- Surface Texture: Look for a bumpy or nodular exterior, indicating potential cavities inside.
- Color: Pay attention to color variations; often, geodes show signs of quartz or calcite deposits on the outside.
- Weight: Generally, geodes will feel heavier than they appear due to the mineral content within.
Resources for Identification
For further exploration and deeper understanding of geodes, here are some useful resources:
- Wikipedia on Geodes
- Britannica insightful articles on rocks and minerals: Britannica
- Engage with fellow collectors on platforms like Reddit for community advice.
- Connect with local groups on Facebook to find geode enthusiasts.
"The beauty of cracking a geode lies not just in what is revealed but in the journey of discovery leading to it."
In summary, this article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of cracking geodes, highlighting key features, identifying techniques, and enriching the experience for collectors. The knowledge shared herein supports not only the act of cracking but the appreciation of these geological treasures.
Prelims to Geodes
Understanding geodes is essential for anyone interested in geology or mineral collection. These intriguing geological formations are not only beautiful but also rich in scientific significance. This section aims to provide clarity on what geodes are and how they form, setting the stage for deeper exploration of their types, gathering methods, and crackin techniques.
Definition and Characteristics
A geode is a hollow rock formation that contains mineral matter. Often, the exterior appears unassuming, with a rough surface, but inside, one can find stunning crystals that have formed over time. The most common minerals found within geodes include quartz, amethyst, and calcite.
Geodes typically range in size from a few centimeters to several meters across. The interior, often lined with crystalline structures, presents a breathtaking display of nature's artistry. Their spherical shape can vary, but they generally have a rounded or oval appearance. The contrasting nature between the dull exterior and vibrant interior makes geodes particularly fascinating to collectors and enthusiasts.
Formation Processes
The formation of geodes is a complex process that spans thousands or even millions of years. They usually form in volcanic or sedimentary rock. The process begins with a cavity inside the rock. Over time, mineral-rich water flows into this space. As the water evaporates, the dissolved minerals begin to crystallize on the walls of the cavity.
Several factors influence how and where geodes form. The type of minerals present, temperature, and pressure all play a role. Different environments can lead to various types of geodes. For example, in volcanic regions, the process may involve gas bubbles in lava, while in sedimentary areas, it could be from mineral deposits in limestone. Understanding these formation processes provides valuable insight into the geologic history of an area and the unique characteristics of the geodes found there.
Types of Geodes
Geodes are structures that encapsulate an intricate world within their hard, often mundane outer layers. Understanding the different types of geodes is crucial for collectors and enthusiasts alike. Each type offers distinct characteristics and variations in appearance and mineral composition, thereby catering to diverse aesthetics and educational interests. This section delves into the notable types of geodes and sheds light on their unique features, making it easier for hobbyists to identify and appreciate them.
Quartz Geodes
Quartz geodes are perhaps the most common and widely recognized type. These geodes typically display a stunning inner layer lined with sparkling quartz crystals. They form when mineral-rich groundwater seeps into volcanic rock cavities. As the water evaporates, it leaves behind silica deposits that crystallize over time.
Characteristics of Quartz Geodes:
- Appearance: Often clear to milky translucent.
- Crystal Formation: Varies in size from tiny druzy crystals to large, well-formed facets.
- Value: Generally affordable yet prized for display due to their clarity and luster.
Benefits of Quartz Geodes:
- They are must-have specimens for beginners due to their abundance.
- Offer excellent learning opportunities about mineral formation and crystal growth.
Amethyst Geodes
Amethyst geodes are another popular type. They have a distinctive purple hue that captivates many collectors. These geodes form similarly to quartz geodes but are specifically composed of amethyst crystals, a variety of quartz.
Characteristics of Amethyst Geodes:
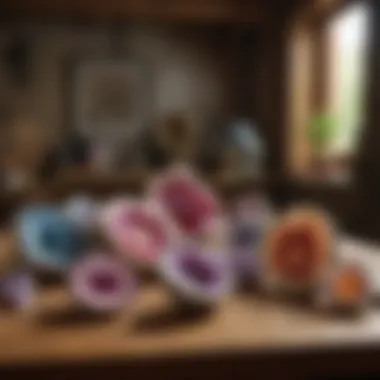
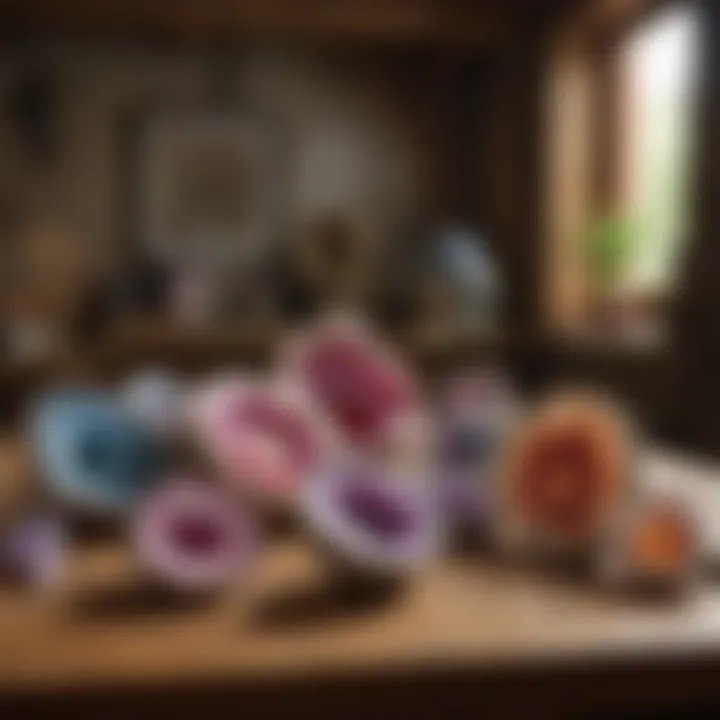
- Coloration: Ranges from light lavender to deep violet.
- Crystal Quality: Often includes well-formed points, showcasing a vivid and rich coloration.
- Market Value: Amethyst geodes can fetch higher prices due to their aesthetic appeal.
Benefits of Amethyst Geodes:
- They are considered to have calming properties, adding metaphysical value.
- Serve as stunning decor items while teaching about the geological processes of formation.
Calcite Geodes
Calcite geodes, while not as common as quartz or amethyst, offer unique aesthetic value. They exhibit creamy, white to orange hues, with a glassy finish. Often, their interiors boast striking calcite crystals that shimmer under light.
Characteristics of Calcite Geodes:
- Appearance: Crystals appear sparkling and are often layered.
- Diversity: Can feature different colors due to impurities, including pink, green, and brown hues.
- Clarity and Luster: Generally less clear than quartz, with a more opaque appearance.
Benefits of Calcite Geodes:
- Adds variety to collections with its distinct coloration.
- Offers insights into the diverse range of mineral compositions in geodes.
Other Notable Varieties
Beyond quartz, amethyst, and calcite, several other notable varieties of geodes exist. Each type provides its own allure and educational value.
Some of these include:
- Celestite Geodes: Characterized by light-blue crystals, ideal for adding a serene look to collections.
- Agate Geodes: Known for their layered, banded appearance, making them visually unique.
- Selenite Geodes: Featuring translucent crystals that provide a luminous quality.
Benefits of Exploring Other Varieties:
- They broaden the mineral collection and offer unique insights into geological diversity.
- Understanding variations helps collectors appreciate the complex processes that result in these natural formations.
"Each geode type not only enriches a collection but also tells a story of the Earth's geological history."
Through this exploration of different types of geodes, collectors can better appreciate the geological beauty and complexity that geodes present. Whether it is enhancing aesthetic appeal or understanding scientific processes, knowing the types of geodes significantly enriches the experience of collecting.
Gathering Geodes
Finding and collecting geodes is an exciting venture for hobbyists and geology enthusiasts alike. The act of gathering geodes serves not only as a practical step in the journey of mineral collection but also as an exploration of the natural world. Understanding where to find these geological wonders and the legalities surrounding their collection is fundamental for anyone interested in this aspect of geology.
Best Locations for Collecting
When seeking to gather geodes, location is critical. Different regions of the world offer a variety of geological formations conducive to the presence of geodes. Some of the most renowned places include:
- Petrified Forest National Park, Arizona: Famous for its petrified wood, this park is also home to agate-filled geodes.
- Southern California: The area, especially around the deserts, has numerous geode sites often found in riverbeds.
- Bentonites Hills, Montana: This region is known for its diverse mineral deposits, including geodes rich in quartz and agate.
- Hot Springs, Arkansas: Not only famous for its thermal springs, but also for geodes with beautiful crystal formations.
Exploration of these areas usually leads to direct encounters with various geodes. Always take into account the geological formations and the conditions that support the formation of geodes.
Legal Considerations
While the thrill of gathering geodes can be memorable, it is essential to be aware of the legal implications. Collecting rocks, including geodes, can be regulated in many jurisdictions. Here are a few key points to keep in mind:
- Check Local Laws: Before embarking on a collecting trip, research the specific laws regarding rock collection in your desired area. Different locations have various regulations.
- Permission Required: Some areas, especially state parks or private lands, may require permission to collect. Ensure you have the necessary permissions before you start.
- Limitations on Quantity: Many places have limits on the amount you can collect each day. This helps ensure the sustainability of geological resources.
"Understanding and respecting legal guidelines in rock collection will ensure that future generations can enjoy the beauty of geodes and other geological formations."
It is advisable to connect with local geological societies or conservation groups, as they can provide valuable information about legalities and ethical collection practices. In sum, gathering geodes is not just about the thrill; it’s about responsibility and stewardship of the natural world.
Essential Tools for Cracking Geodes
Cracking geodes is an activity that demands both preparation and the right tools. Having the essential tools on hand ensures a successful and safe experience when you embark on opening these geological treasures. This section delves into the specific tools needed, discussing their unique benefits and considerations, focusing on protective gear, precision tools, and inventive methods that can enhance your cracking experience.
Protective Gear
Safety is of utmost importance when cracking geodes. One must consider protective gear as the first line of defense against potential accidents. The task presents risks, including flying rock shards and exposure to dust.
- Safety Goggles: Protects the eyes from debris. It is vital to wear goggles specifically rated for impact. This ensures that any pieces that chip off do not cause injury.
- Gloves: Heavy-duty gloves can safeguard hands against sharp edges. This is particularly significant if a geode fractures unexpectedly, as the pieces can have jagged edges that can cause cuts.
- Face Mask: A face mask protects against dust generated during the cracking process. This can have a significant health benefit, especially during the initial impacts.
By using protective gear, one can greatly mitigate the risks involved.
Precision Tools
Once safety is assured, attention shifts to precision tools. These tools ensure that the process of cracking geodes is efficient and less destructive to the surrounding matrix. Key precision tools include:
- Geode Hammer: A specialized hammer designed for geodes is often recommended. These hammers are heavier than standard hammers, allowing for focused, precise strikes that can effectively crack the geode without excessive force.
- Chisel: A chisel can be used in conjunction with the hammer to create strategic fractures in the geode. By inserting the chisel into a natural seam and tapping it with the hammer, the risks of shattering the entire geode decrease.
- Wet Saw: For a more advanced approach, a wet saw can be exceptionally useful. While more expensive, a wet saw allows for clean cuts and reduces dust and flying debris, making it an excellent investment for serious collectors.
Using these precision tools, one can enjoy a better experience while preserving the beauty of the geode.


Alternative Methods
If traditional tools do not appeal, alternative methods can also yield satisfying results. These methods may vary in effectiveness but can be interesting to explore. Some notable options include:
- Soaking: Placing a geode in water for a few days may weaken the bonding within. While this method is not guaranteed to work for every geode, it can be a gentle introduction to opening them without force.
- Freezing: Another method involves freezing the geode. The expansion of water when it freezes could create fractures. Though this method requires experimentation, it offers an alternative route to geode cracking that some find satisfying to try.
- Chemical Solutions: There are products available that help to break down minerals in some geodes. This is a more complex method but can be suitable in cases where other techniques prove challenging.
Ultimately, the method of cracking geodes should be selected based on the tools available and the specific type of geode being opened.
The right tools not only enhance the accuracy and cleanliness of cracking geodes, but they also prioritize safety, ensuring that rock collectors enjoy this fascinating process without unnecessary risk.
Techniques for Cracking Geodes
Understanding the techniques for cracking geodes is crucial because it directly affects how successfully you can reveal the stunning formations hidden inside. Each method has its own advantages and precautions, catering to different skill levels and available tools. When practiced diligently, these techniques enhance not only the safety of the process but also ensure minimal damage to the geode itself, preserving its integrity. Ultimately, knowing the appropriate method can transform a simple hobby into a rewarding exploration of geology.
Traditional Methods
Traditional methods rely on manual tools and techniques passed down through generations. These approaches often emphasize the connection between collector and collected, demanding patience and care.
- Choosing a Suitable Geode: Before starting, selecting a geode is critical. Look for those with a more rounded shape; irregular shapes can complicate the cracking process.
- Assessing the Size: Larger geodes may require more robust techniques, while smaller ones can often be cracked with less force.
- Positioning the Geode: Place the geode on a solid surface, like a rock or a piece of wood, to absorb vibrations and prevent it from bouncing away when struck.
One of the traditional methods involves wrapping the geode in a cloth to limit scattering pieces. This can help control sharp shards that might fly off during the cracking process, ensuring a safer environment.
Using a Hammer
Using a hammer is a straightforward technique for those who prefer direct action. This method can be effective for the casual collector. Here are some key points to consider:
- Selecting the Right Hammer: A regular household hammer can work, but a geology hammer with a pointed end is ideal for precision.
- Striking Technique: A firm, controlled strike is advisable. Start with light taps and gradually increase strength if the first attempt does not produce a crack. Hitting too hard at first can shatter the geode into many high-speed fragments.
- Listening to Changes: As you strike, listen for changes in sound. A dull thud typically indicates that the geode has not cracked, while a clearer ring may indicate a successful fracture.
Tip: Always wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from any potential flying fragments.
Wet Saw Techniques
For those who desire precision or wish to showcase the inner beauty of large geodes, a wet saw can be an effective tool. The use of a wet saw requires an understanding of both the mechanics and the benefits it offers.
- Water Cooling: The wet saw employs water to cool the blade, reducing the heat generated during the cutting process. This prevents any thermal stress that could crack the geode unevenly.
- Sturdiness: Be sure to secure the geode firmly in place before you begin cutting. An unstable piece can affect the quality of the cut.
- Step-by-step Approach: Start with shallow cuts and gradually deepen them, taking care to follow the natural lines of the geode. Rushing the process typically leads to mistakes that can damage the specimen.
Safety Precautions
When engaging in the process of cracking geodes, safety precautions should be a top priority. The potential for injury is significant when using tools that can generate flying debris or exert substantial force. The act of breaking these geological formations requires not just skill but also a mindful approach to safety to prevent accidents. Failure to adhere to safety protocols can result in serious injuries or damage to valuable specimens.
Protective Equipment Overview
A variety of protective equipment is necessary to ensure a safe experience while cracking geodes. The most essential items to consider include:
- Safety goggles: These protect the eyes from shards of rock and dust that can become airborne when a geode is struck.
- Gloves: Thick, sturdy gloves can shield the hands from sharp edges and provide a better grip on tools, reducing the risk of slippage.
- Face shield: In addition to goggles, a face shield offers extra facial protection against flying particles.
- Steel-toed boots: Wearing proper footwear prevents foot injuries that may occur if heavy tools are dropped.
By using these pieces of equipment, enthusiasts can significantly decrease their risk of injury during the process, allowing a safer, more enjoyable experience.
Workspace Safety Considerations
Creating a safe workspace is critical for the successful cracking of geodes. A well-organized area not only contributes to safety but also enhances efficiency. Key elements to consider include:
- Flat Surface: Ensure the geodes are placed on a stable, flat surface to prevent them from rolling or moving unexpectedly.
- Minimize Clutter: Remove distractions and unnecessary items from the workspace to reduce the risk of accidents.
- Ventilation: Proper airflow helps eliminate dust and fumes, especially if using any power tools.
- Clear Space: Maintain an adequate distance from other people and pets to ensure safety during the breaking process.
Taking these precautions when setting up your workspace ensures that you can focus solely on the task at hand without the burden of safety worries.
Safety should never be an afterthought in geological exploration. The measures you take today can prevent accidents that could tarnish the joy of discovering the beauty inside a geode.
Best Practices for Preservation
Preserving geodes is vital for both aesthetic and scientific reasons. They represent unique geological formations that have taken thousands of years to create. Proper preservation techniques ensure that these natural wonders retain their beauty while also maintaining their structural integrity. By following best practices for preservation, collectors can safeguard their specimens for future generations and enhance their overall enjoyment of these geological artifacts.
Cleaning Techniques
Cleaning geodes requires careful consideration to avoid damaging delicate surfaces. Using incorrect methods can lead to loss of luster or even structural damage. Here are essential techniques for cleaning:
- Soft Bristle Brush: This is ideal for removing loose dirt and debris without scratching the surface of the crystal.
- Water and Mild Detergent: A mild dish soap mixed with water can effectively clean geodes. It is crucial to avoid harsh chemicals that may harm the stones.
- Ultrasonic Cleaners: Some collectors opt for ultrasonic cleaners to remove stubborn dirt. However, this method is suitable only for geodes without delicate features.
- Air Drying: After cleaning, allow the geodes to air dry completely. Storing damp geodes can promote mold growth.
Regular cleaning can preserve both the appearance and the value of the geode. Collectors should handle their specimens with care to prevent any unintentional damage during the cleaning process.
Displaying Your Geodes
Displaying geodes appropriately is as essential as cleaning them. Proper display not only showcases the beauty of each piece but also protects them:
- Display Cases: Enclosed display cases can protect geodes from dust and physical damage. Displaying the geodes under glass allows for unobstructed views while keeping them secure.
- Shelving: If using open shelves, ensure the geodes are positioned securely and away from areas where they might easily fall.
- Lighting Considerations: Natural light is beautiful but can fade colors over time. Soft, diffused lighting is generally best for preserving the colors of the geodes without risking damage.
- Labeling: Providing information about each geode, such as its origin or mineral composition, can enhance the educational value for viewers.

Proper display is a part of the overall appreciation of these geological wonders. It can elevate the experience for both the collector and the viewer.
Educational Value of Geodes
Geodes serve not only as objects of beauty but also as powerful tools for education in the field of geology. Understanding geodes provides significant insight into geological processes and the natural world. Studying geodes allows enthusiasts and collectors to explore concepts such as mineral formation, crystallography, and the variety of conditions that lead to the creation of such unique formations.
For many, the journey of cracking a geode is as fascinating as the final product. It offers hands-on learning experiences that can deepen appreciation for Earth sciences. Knowing about geode formation enhances the way collectors perceive their specimens, turning a simple hobby into a comprehensive exploration of mineralogy.
"Geodes are portals to understanding the Earth's history, showcasing the delicate balance of geological forces at play."
Geological Significance
Geologically, geodes can reveal important information about the environment in which they formed. They are found in sedimentary, igneous, and volcanic rock, indicating diverse geological settings. Each type of geode showcases different minerals and structures that can provide valuable information on the temperature and pressure conditions during their formation. For instance, quartz geodes often indicate significant silica activity, while amethyst geodes can offer insights into the presence of iron during their crystallization.
Learning about these minerals infuses enthusiasts with knowledge of mineralogical properties as well as the processes that lead to geode formation, including:
- Mineral crystallization – Understanding how minerals crystallize can guide collectors in identifying minerals from their outward appearance.
- Rock formation – Geodes often form in gas bubbles within volcanic ash or sedimentary layers, linking them to relevant geological events.
- Environmental clues – The types of minerals present can inform collectors about ancient environments.
These elements emphasize the educational value of engaging with geodes beyond mere collection, inviting deeper scientific inquiry.
Learning Opportunities
Geodes offer various opportunities for learning that extend beyond geology. For educators, they represent an engaging method for teaching various scientific concepts in a hands-on manner. Cracking a geode can be an exciting classroom project, fostering inquiry-based learning and encouraging students to explore physical sciences in a tangible way.
Potential learning opportunities include:
- Scientific methodology - Engaging with geodes allows students to practice scientific methods by hypothesizing about geode contents and testing those hypotheses through cracking and observation.
- Critical thinking - Each geode presents potentially different results, encouraging learners to analyze and make deductions based on mineral types, colors, and formations.
- Integration of subjects - Concepts from chemistry and art can be integrated when discussing mineral compositions and aesthetic appreciation of crystals.
Geodes, therefore, act as an intersection of various learning paths, demonstrating that science is not just about theory but also about exploration and discovery.
These educational benefits make geodes particularly appealing to rock and fossil collectors, who can appreciate both their beauty and significance in shaping our understanding of the Earth.
Community and Enthusiast Networks
The realm of geode cracking extends beyond the personal journey into the world of geology. Engaging with community and enthusiast networks is essential for collectors. Such interactions provide access to a wealth of shared knowledge and experiences, enriching one’s understanding and appreciation of geodes.
When you join a community, you connect with like-minded individuals who share similar interests. This connection fosters an environment of learning, where enthusiasts can exchange tips and techniques for cracking geodes, identifying various types, or even sourcing rare specimens. Sharing insights can dramatically enhance one’s skillset and deepen the overall experience of collecting.
Joining Geology Clubs
Geology clubs serve as a foundation for local geological communities. These clubs often organize field trips and hands-on workshops where members can practice cracking geodes together. This practical approach not only hones skills but also builds lasting relationships among members.
Participating in these clubs can provide several benefits:
- Access to Resources: Members often share tools and locations for collecting.
- Expert Guidance: Many clubs have experienced members who can offer valuable advice.
- Community Events: Regular events promote a sense of belonging.
- Knowledge Exchange: Members can share their unique experiences, which enhances collective learning.
Additionally, clubs often have affiliations with broader geological organizations, granting members access to events and publications that keep them informed about the latest in geology.
Online Resources for Collectors
In today’s digital age, online resources are invaluable for geode enthusiasts. Various platforms host forums, websites, and social media groups dedicated to rock and mineral collecting.
Key advantages of online communities include:
- Global Reach: Connect with collectors worldwide, sharing diverse knowledge and experiences.
- Instant Access: Online resources provide immediate information, which is especially helpful when identifying new specimens.
- Online Marketplaces: Many collectors sell or trade tools and geodes through these platforms.
Popular online resources include:
- Reddit communities, which facilitate discussions and Q&A.
- Facebook groups for active engagement with fellow collectors.
- Educational websites like wikipedia.org and britannica.com for deeper learning.
The more you involve yourself in communities, the richer your journey into the world of geodes will be.
Overall, both local geology clubs and online resources offer robust networks for collectors, making the process of cracking geodes not only a solitary activity but also a shared, enriching experience.
Closure
The conclusion serves a vital role in encapsulating the essence of this article. It brings together the significant insights acquired about geodes, their formation, and the means to crack them open safely. Understanding the various types of geodes, their characteristics, and the processes involved in their formation enhances the appreciation of these natural wonders. Furthermore, the practical techniques discussed for cracking and preserving geodes allow hobbyists and collectors to engage meaningfully with their specimens.
Summarizing Key Points
In summary, a few key points surface throughout this exploration:
- Definition and Characteristics: Geodes are hollow rock formations with mineral-lined interiors, showcasing stunning crystalline structures.
- Formation Processes: They form through specific geological processes over millions of years, often involving volcanic and sedimentary activity.
- Types of Geodes: Various types exist, including quartz, amethyst, and calcite geodes, each featuring unique attributes.
- Essential Tools: Proper tools such as hammers, safety gear, and possibly wet saws are crucial when cracking geodes to avoid injury and ensure success.
- Safety Precautions: The importance of protective equipment and workspace safety cannot be understated when engaging in this activity.
- Educational Value: Geodes offer remarkable educational insights into geology, which can deepen one's interest and knowledge.
Understanding these elements not only equips collectors with the knowledge necessary for responsible collecting but also enriches their experience.
Encouragement for Further Exploration
As you conclude your reading, consider this an invitation to delve even deeper into the world of geology and geodes. Whether through joining geology clubs, participating in local field trips, or engaging with online communities like Reddit or Facebook, the opportunities for learning and connection are abundant.
Expanding your knowledge can lead to new discoveries, and you may find unexpected gems in both your collection and your experiences. Explore scientific literature, visit museums, and connect with fellow enthusiasts who share your passion. The world of geodes is vast and filled with wonder, offering endless avenues for exploration.



